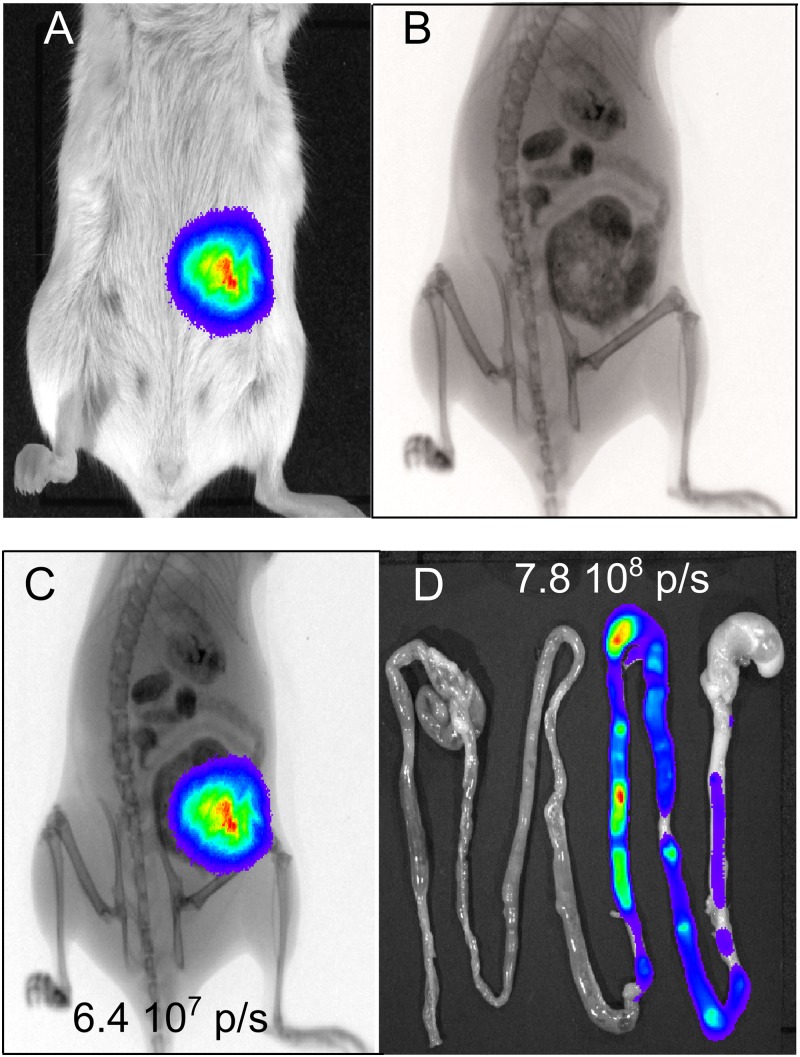
Fig 2.
Monitoring of intestinal transit of L. lactis and L. plantarum by bioluminescence imaging in whole animals. L. lactis-CBRluc, L. plantarum-CBRluc, and L. lactis-lux (5 × 1010 CFU) was inoculated intragastrically into mice, and the bioluminescent signal was measured transcutaneously in whole animals at different time points postfeeding. (A) The intensity of the transcutaneous photon emission is represented as a pseudocolor image. (B) The same mouse was imaged in X-ray mode after barium sulfate administration. (C) The mouse was imaged in both bioluminescence and X-ray modes, and the bioluminescent signal was quantified in the whole animal. (D) The digestive tract of the mouse was then dissected after sacrifice, and the bioluminescent signal was quantified on intact organs. A representative mouse is shown.