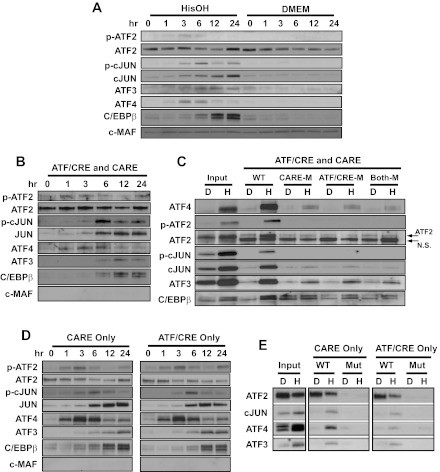
Fig. 5.
ATF4 and cJUN bind to both the CARE and ATF/CRE sites in the ATF3 promoter during the AAR. A: the cellular protein content of the indicated bZIP transcription factors was analyzed by immunoblot in HepG2 human hepatoma cells incubated for 0–24 h in control medium (DMEM) or DMEM containing 2 mM HisOH. The cMAF protein is not regulated by the AAR and was used a negative/loading control. B: DNA affinity precipitation assay (DAPA) analysis for protein binding to sequences within the human ATF3 promoter was measured using a oligonucleotide containing the WT ATF3 promoter sequence covering both the CARE and ATF/CRE regions (nt −104/+27). Nuclear protein extracts from HepG2 cells maintained for 0–24 h in DMEM + 2 mM HisOH were incubated with the ATF3 promoter DNA sequence bound to agarose beads. After protein elution from the agarose-bound DNA, the proteins were analyzed by immunoblot for the basic region leucine zipper (bZIP) proteins indicated. Equal loading of the samples was established by Fast Green staining of the blot (not shown). C: DAPA analysis for protein binding was measured using the following oligonucleotides: WT nt −104/+27 (WT), CARE site mutated (CARE-M), ATF/CRE site mutated (ATF/CRE-M), or both sites mutated (Both-M). The nuclear extracts were from cells that had been incubated in DMEM (D) or DMEM + 2 mM HisOH (H) for 6 h. After protein elution, bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting along with an aliquot of the starting nuclear extract (Input). D: DAPA analysis for protein binding was measured using an oligonucleotide covering the region of the human ATF3 promoter containing either the CARE sequence only (nt −33/−5) or the ATF/CRE sequence only (nt −103/−75). Nuclear protein extracts from HepG2 cells maintained for 0–24 h in DMEM + 2 mM HisOH were incubated with the indicated ATF3 promoter DNA sequence. After protein elution, bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. E: DAPA analysis for transcription factor binding was performed using the oligonucleotides described for D, except that a 2nd oligonucleotide for each contained mutations in the CARE or ATF/CRE sequence. The nuclear protein extracts were prepared from HepG2 cells maintained for 6 h in DMEM (D) or DMEM + 2 mM HisOH (H). After the binding incubation, the eluted proteins were subjected to immunoblotting along with an aliquot of the starting nuclear extract (Input). Fast Green staining of the blots established equal loading of the lanes (not shown). Each panel shows a representative blot from 2–3 independent experiments.