Figure 9.
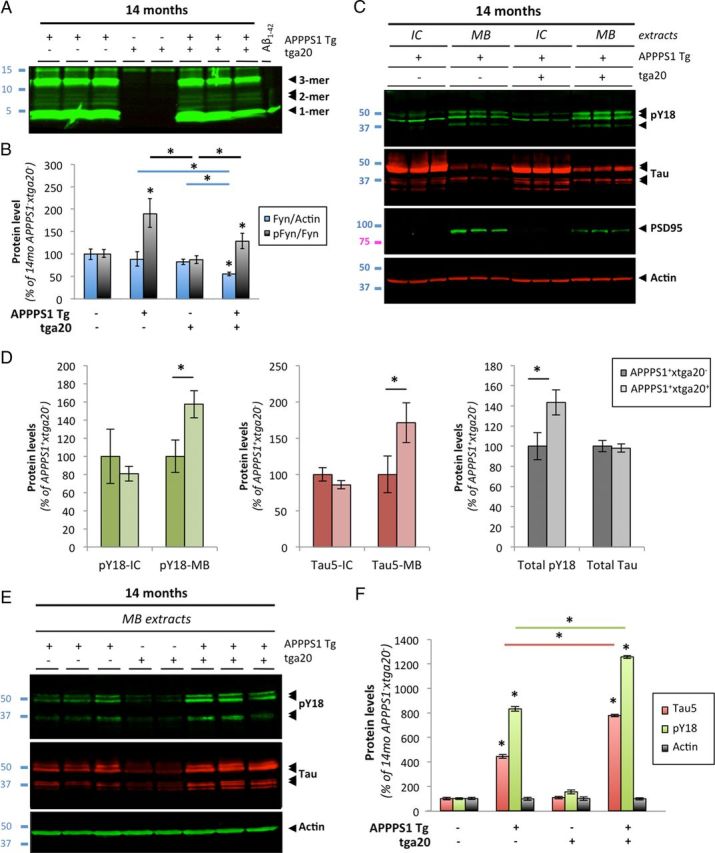
Aβ-induced activation of Fyn and tau hyperphosphorylation is enhanced in aged APPS1 mice overexpressing PrP. A, Soluble brain levels of low-molecular-weight Aβ oligomers in 14-month-old APPPS1×tga20 mice was assessed by quantitative Western blot (WB) using 6E10. B, Quantification of total Fyn, pY416-Src, and actin protein levels in 14-month-old mice (APPPS1−×tga20−, APPPS1+×tga20−, APPPS1−×tga20+, and APPPS1+×tga20+) following WB. A marked elevation of pY416-Fyn was observed in APPPS1+×tga20+ compared with APPPS1−×tga20+ mice. C, Tau missorting was illustrated by biochemical segregation of pY18-Tau, total tau, PSD95 in IC versus MB extracts using Western blotting. D, Quantification of PY18-tau and total tau immunoreactivity across protein fractions and genotypes. Aged APPPS1+×tga20+ mice showed a ∼1.8-fold accumulation of tau and a ∼1.6-fold increase in phosphorylation at Y18 compared with age-matched APPPS1+×tga20− mice. E, Enhanced accumulation of full-length tau and cleavage products phosphorylated at Y18 in PSD95-containing extracts of old APPPS1+×tga20+ mice. Actin was used as internal standard. F, Quantification of tau species immunoreactive for Tau5 and PY18 in 14-month-old APPPS1−×tga20−, APPPS1+×tga20−, APPPS1−×tga20+, and APPPS1+×tga20+ mice (bars represent the mean ± SD; *p < 0.05, ANOVA followed by Student's t test; n ≥ 3 animals/genotype/age/experiment).
