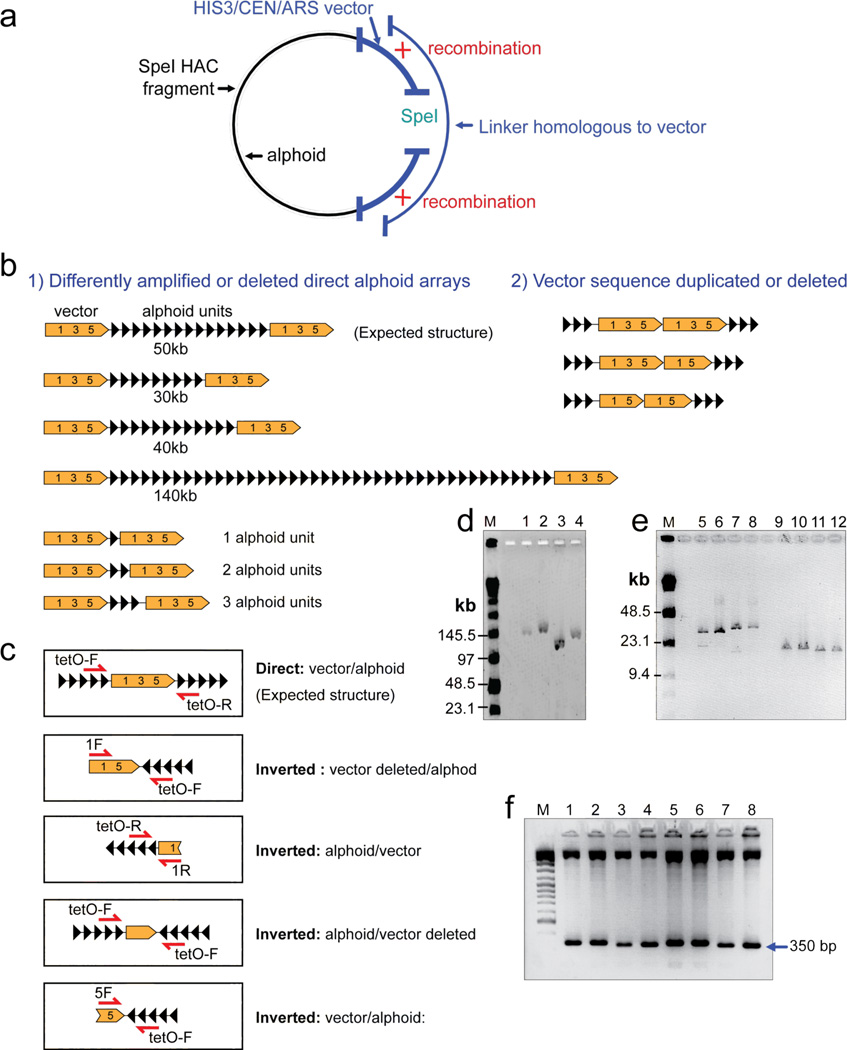
Figure 3.
Structural analysis of the HAC fragments rescued by TAR cloning in yeast. (a) A scheme of rescue of the SpeI HAC fragments as circular molecules by transformation-associated homologous recombination in yeast. The vector part of input DNA contains a YAC cassette with an yeast selectable marker HIS3, ARS and CEN sequences. In vivo recombination between a HAC fragment and a linker results in a circular molecule. The clones with the circularized fragments were selected on SD-His− medium. Alphoid DNA is marked in black. Vector DNA is marked in blue. (b) Schematic diagram of the rearranged input DNA molecules rescued in yeast and E. coli. Several examples of SpeI-fragments rescued in yeast are shown. (c) PCR analysis of direct and inverted alphoid sequences in the rescued YAC clones and in the alphoidtetO-HAC propagated in chicken cells. A single tetO-F primer amplifies a part of the vector sequence (positions 2,913–3,300 in the RCA/SAT/43 vector) flanked by inverted alphoid repeats. (d, e) Characterization of the rescued clones in a BAC form. BAC DNAs were isolated from 12 randomly chosen clones, digested by SpeI for linearization, separated by CHEF gel electrophoresis (lanes 1, 2, 3, 4 with range 20–300 kb; lanes 5–12 with range 10–70 kb), and visualized by staining with ethidium bromide. M - Pulse Marker™ 0.1–200 kb (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). (f) The tandem repeat structure of alphoid arrays is confirmed by StuI restriction enzyme digestion (350 bp alphoid dimer unit); the upper bands represent vector fragments.