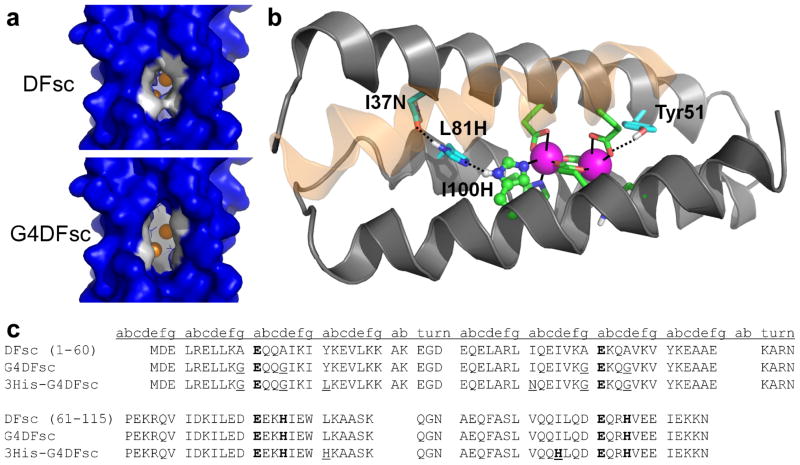
Figure 1.
Important structural features of and amino-acid sequences for the original and redesigned DFsc proteins. (a) Surface models of DFsc (top) and G4DFsc (bottom) based on the initial DFsc computational design.21 The four Ala to Gly substitutions (shown in white) significantly open the substrate access channel. (b) Structure of 3His-G2DFsc variant (PDB 2LFD) highlighting the added active-site His residue (H100) and supporting mutations (I37N and L81H). The helix closest to the viewer is shown as transparent to allow for viewing of the ligands. Note that the structure shown is for a variant with two Ala and two Gly residues along the substrate access channel which proved more stable during the extended data collection times required for the structure determination. This variant still exhibited N-oxygenase activity, but to a lesser extent than 3His-G4DFsc. (c) Amino acid sequences for DFsc, G4DFsc, and 3His-G4DFsc. Metal-binding residues are bolded and mutations introduced are underlined.