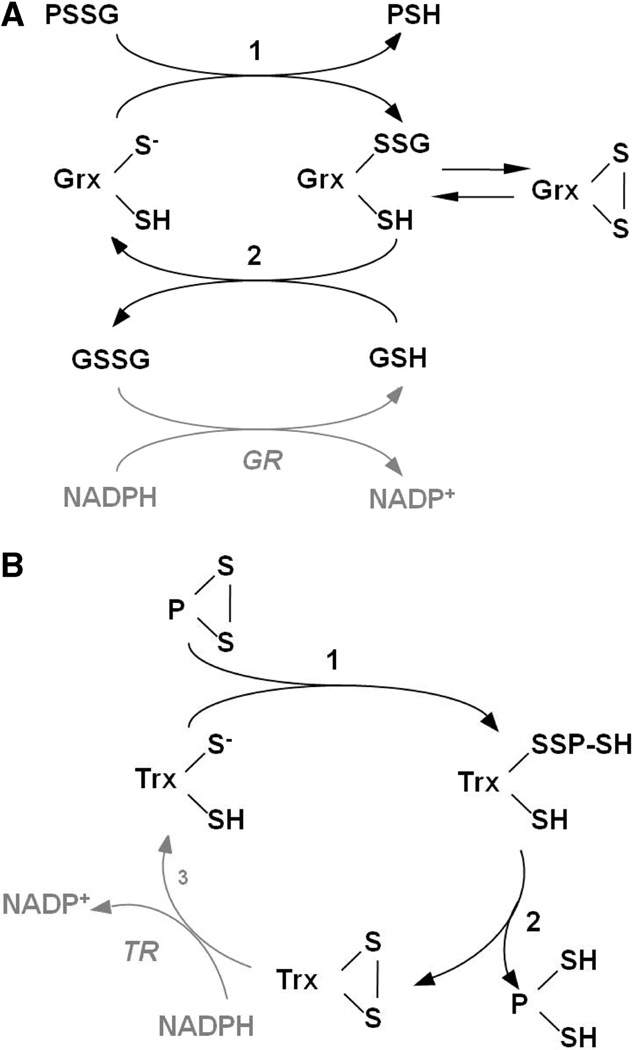
Scheme 1.
(A) Catalytic Mechanism of Protein Deglutathionylation by Mammalian Grx1 (16, 18) and Grx2 and (B) Catalytic Mechanism of Intramolecular Disulfide Reduction by Mammalian Trx (5, 57)a
a In the first step of panel A, the catalytic cysteine thiolate of Grx attacks the glutathionyl sulfur of the protein–SSG mixed disulfide, releasing the first product, protein–SH. In the second step of the reaction, GSH attacks the enzyme–SSG intermediate, restoring the reduced enzyme and releasing GSSG. Alternatively, the cysteine adjacent to the active site may attack the Grx–SSG intermediate, forming an intramolecular disulfide and releasing GSH. The intramolecular disulfide may be recruited back into the catalytic cycle by reaction with GSH, re-forming Grx–SSG, and proceeding with step 2. Reduction of GSSG is catalyzed by GSSG reductase, coupled to oxidation of NADPH. PSSG, protein–GSH mixed disulfide. In the first step of panel B, the acidic cysteine thiolate of Trx attacks an intramolecular protein disulfide, forming a transient HS–Trx–SS–protein–SH intermediate in which the second active site cysteine of Trx attacks the intermolecular disulfide and displaces protein–(SH)2, forming the Trx–(S)2 intramolecular disulfide. Trx disulfide is then reduced by Trx reductase (TR), coupled to oxidation of NADPH. P, protein.