Fig. 2.
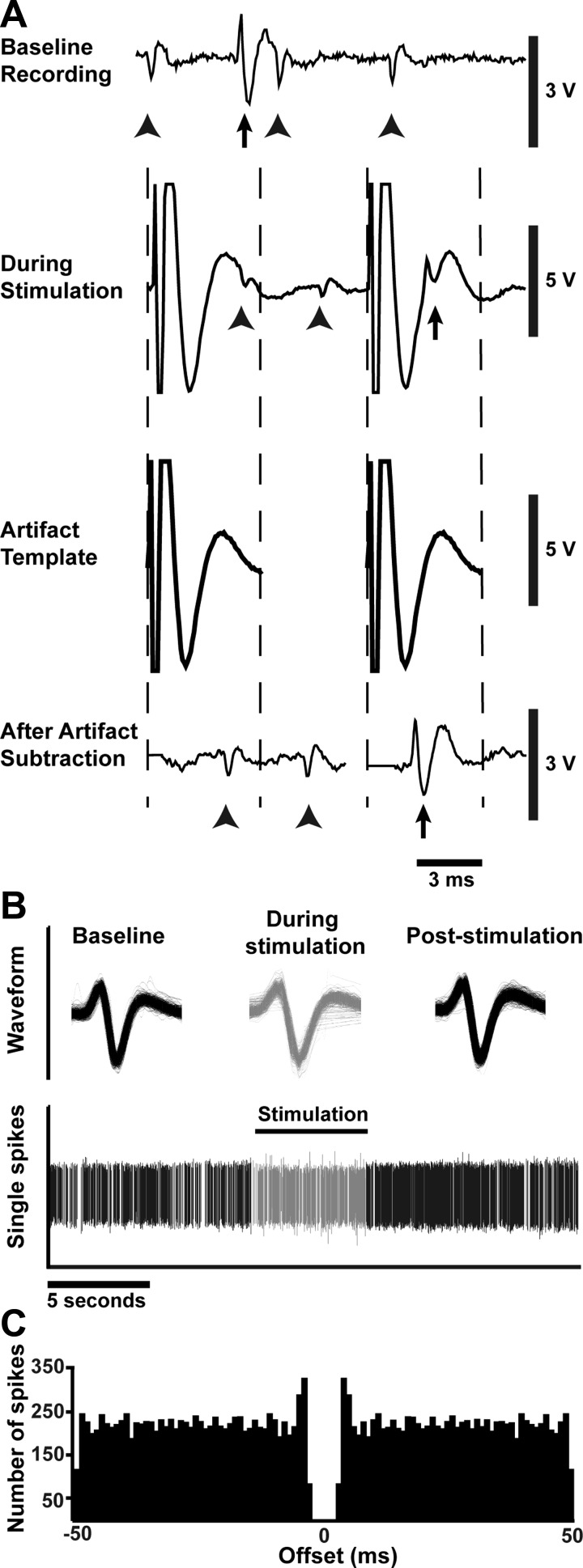
Template subtraction, spike sorting, and waveform analyses allow individual action potentials to be discerned during stimulation with a high degree of confidence. A: in an example of artifact removal, at baseline, 2 distinct action potential waveforms are distinguishable (arrows and arrowheads indicate the 2 waveforms). During stimulation, a large artifact prevents distinguishing neuronal activity or matching action potentials to previously identified waveforms, but after subtraction, waveforms are again distinguishable. B: action potential waveforms are overlaid to show continuity of recording from a single neuron after artifact removal throughout the entire stimulation trial. Spikes recorded before and after stimulus train are shown in black; those during the stimulus train in gray. C: in this example autocorrelogram, the refractory period around time 0 and surrounding short-term peaks indicate that only a single neuron was under consideration during the recording (Bar-Gad et al. 2001; Montgomery 2006).