Fig. 2.
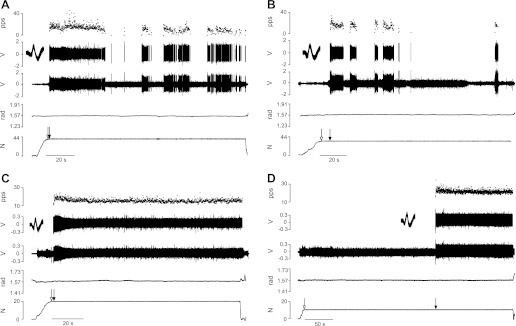
Motor units discharged action potentials either intermittently or repetitively at recruitment. A–D, from top to bottom: instantaneous discharge rate of the motor unit (pulses per second, pps), discriminated action potentials with waveform overlay, interference EMG from the wire electrode, electrogoniometer measurement of elbow angle, and signal from the force transducer in series with the load. The 4 panels show the 2 discharge patterns (intermittent and repetitive) observed when there were small and large differences between the target force and the recruitment threshold force of the motor unit. The motor unit from a young adult shown in A and B discharged intermittently for both small (A) and large (B) differences between the 2 forces. The motor unit from an old adult shown in C and D discharged repetitively for both small (C) and large (D) target-force differences. Open arrows indicate the start of the task; filled arrows denote the onset of motor unit activity.
