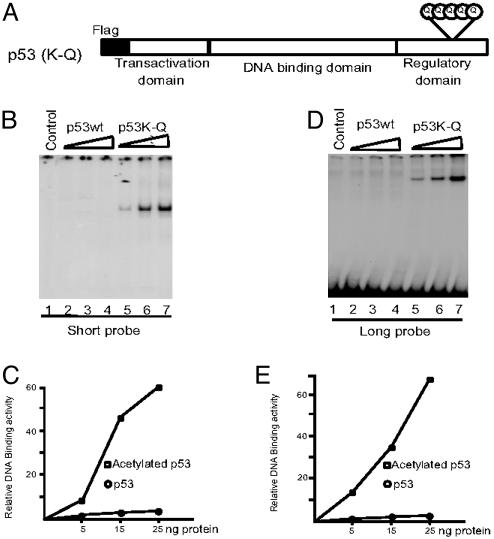
Fig. 2.
Lysine to glutamine mutations in the p53 C terminus enhance DNA binding activity in vitro.(A) Schematic representation of the p53 (K-Q) mutant with lysine to glutamine changes at residues 370, 372, 373, 381, and 382. (B and C) EMSA assay of p53 wild type (wt) (lanes 2–4) and p53 (K-Q) mutant (lanes 5–7) with short probe (B). The resulting DNA-protein complexes in B were quantitated by phosphorimaging by using imagequant software (C). (D and F) EMSA assay of p53 wt (lanes 2–4) and p53 (K-Q) mutant (lanes 5–7) with long probe (D). The resulting DNA–protein complexes in D were quantitated by phosphorimaging by using imagequant software (F).