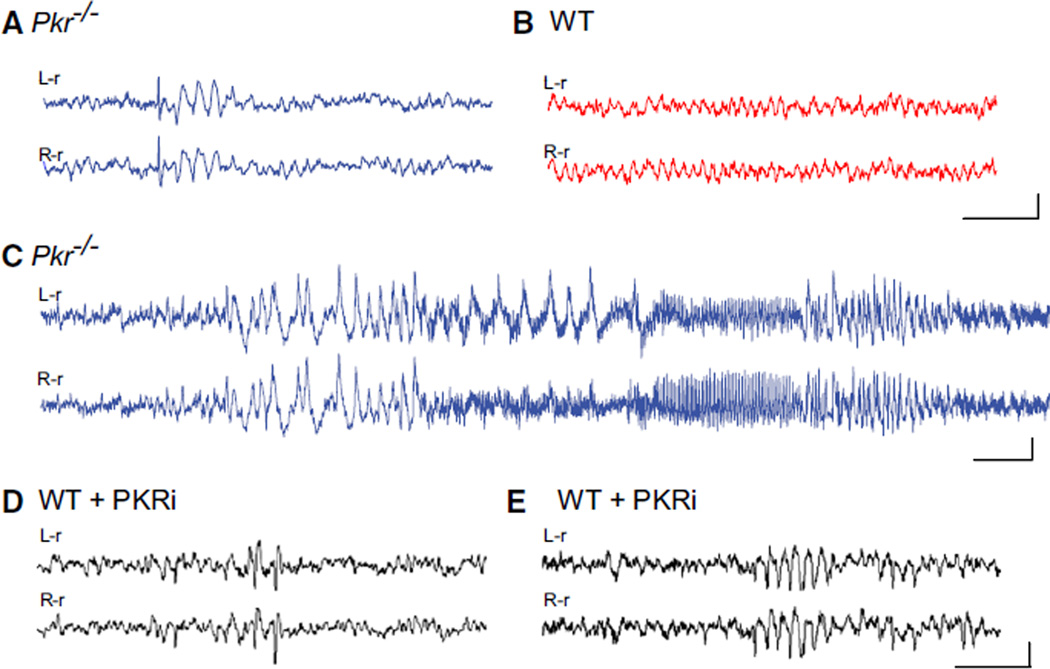
Figure 1. Synchronized EEG Activity in Pkr−/− Mice or WT Mice Treated with PKRi In Vivo.
(A–C) Traces from bilateral cortical electrodes (left hemisphere reference, L-r; right hemisphere reference, R-r) show abnormal synchronous activity, including solitary interictal spikes followed by brief wave discharges (A) and electrographic seizures (C) in freely moving Pkr−/− mice, but not in WT mice (B).
(D and E) Injection of PKR inhibitor (PKRi; 0.1 mg/kg i.p.) induced acute spiking (D) and rhythmic bursts (E) in adult WT mice. Calibration: 1 s and 200 µV. Abnormal EEG activity was absent from all WT control recordings (n = 7) but present in all Pkr−/− mice (n = 10) and in six out of seven PKRi-injected mice (recorded 1 hr after of PKRi injection). By Fisher’s exact test, p values were < 0.001 and < 0.01, respectively.
For additional information, see Movie S1. See Figure S1 for lack of change in brain morphology; Figure S6B for EEG interictal spikes in mice with constitutively reduced eIF2α phosphorylation (eIF2α+/S51A mice); and Figure S7D for the effect of PKRi in vivo.