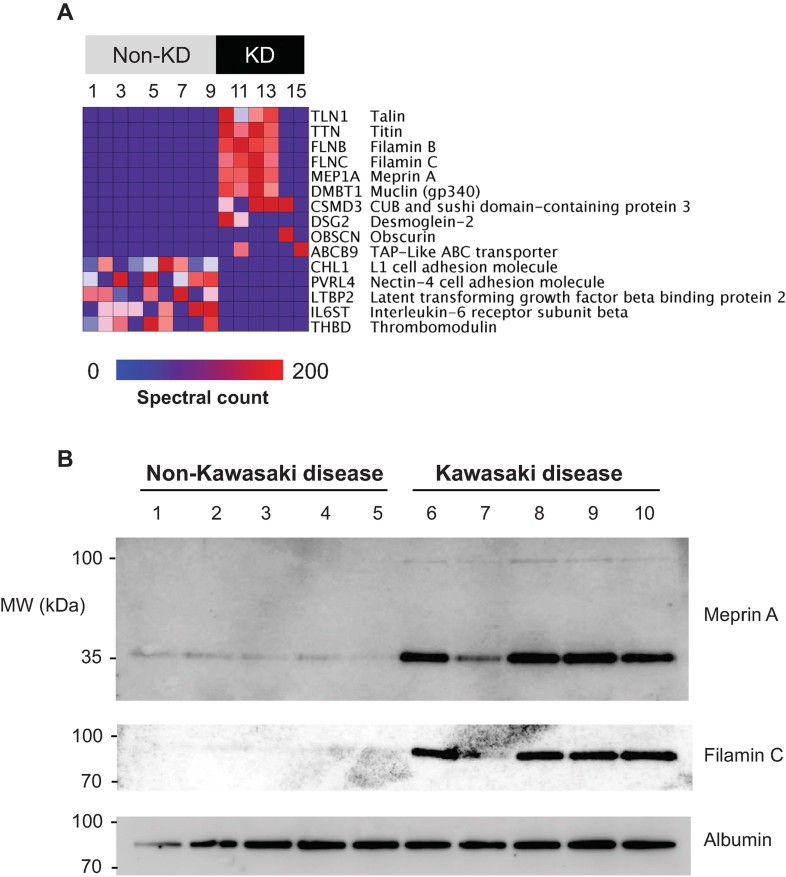
Figure 1. Patients with Kawasaki disease exhibit a unique urine proteome that is distinct from patients without KD or commonly present urinary proteins.
- Heatmap of the 15 individual urinary proteomes (columns) showing the results of Bayesian analysis of the top 10 proteins (rows) that are detected in patients with KD as compared to those without. The top 5 proteins that are detected in patients without KD as compared to those with KD are shown for comparison. Blue-to-red colour gradient represents the number of MS/MS spectra (spectral count) that corresponds to urinary protein abundance.
- Western immunoblot analysis of meprin A and filamin C in urine, demonstrating enrichment of meprin A and filamin C in the urine of patients with KD as compared to patients without KD. Note that meprin A and filamin C are detected predominantly as partial-length isoforms, with apparent molecular weights of 35 and 80 kDa, respectively. Albumin serves as the loading control.