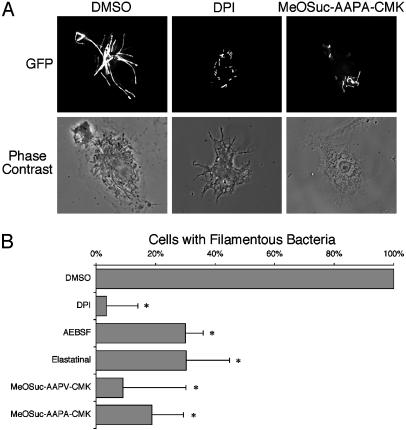
Fig. 1.
Serine protease inhibitors decrease bacterial filamentation in BMDM. (A) Immunofluorescence. BMDM were pretreated with inhibitors, infected with S. typhimurium expressing GFP for 24 h, and then examined by fluorescence microscopy. Mock-treated cells contained filamentous bacteria (GFP, DMSO). There was a decrease in the number of filamentous bacteria in cells treated with chemical inhibitors of ROIs (DPI) or elastase-like serine proteases (MeOSuc-AAPA-CMK). n ≥ 4. (B) Quantification. Cells were treated as described in A, and the percentage of infected macrophages containing filamentous bacteria were quantified in at least 100 infected cells per experiment. The mean percentage of infected DMSO-treated cells containing filamentous bacteria (24 ± 5%; n = 6) was normalized to 100%. *, P < 0.01; n ≥ 4.