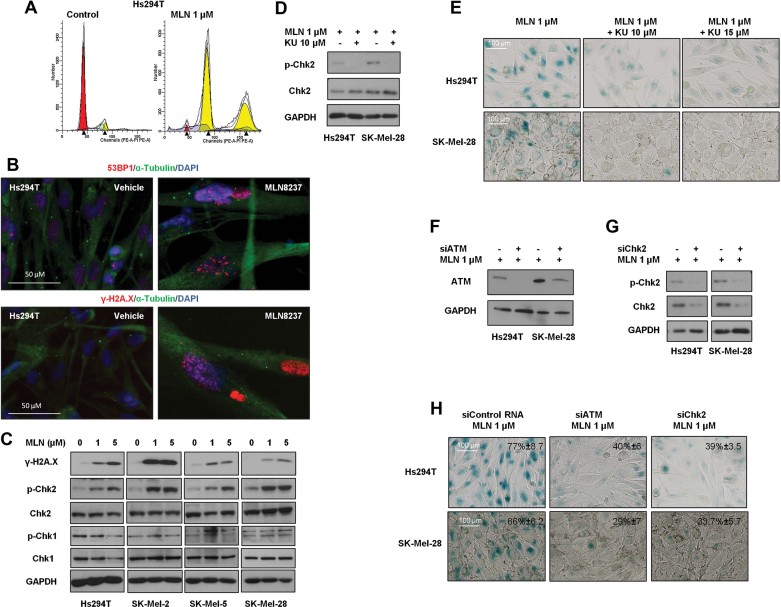
A. Hs294T cells were treated with 1 µM MLN8237 or vehicle control for 2 days and DNA content was examined by FACS.
B. Hs294T cells were treated with 1 µM MLN8237 or vehicle control for 5 days. After treatment, 53BP1 and γ-H2A.X were evaluated by immunocytochemistry. Cell nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst dye, and the samples were visualized by microscopy.
C. Hs294T, SK-Mel-2, SK-Mel-5 and SK-Mel-28 cells were treated with vehicle alone, 1 or 5 µM MLN8237 for 5 days, and the levels of γ-H2AX, p-Chk2, Chk2, p-Chk1 and Chk1 were analysed by Western blot.
D,E. Hs294T cells and SK-Mel-28 cells were treated with 1 µM MLN8237 with or without the ATM inhibitor KU-55933 at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. After treatment, the level of p-Chk2 was examined by Western blot (D) and senescence was determined by β-galactosidase staining (E).
F–H. Hs294T cells and SK-Mel-28 cells were transfected with siATM or siChk2. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were treated with 1 µM MLN8237 for 3 days. Levels of ATM (F), p-Chk2 and Chk2 (G) were analysed by Western blot. Senescence after transfection of siATM or siChk2 was evaluated by β-galactosidase staining and representative photomicrographs are shown (H). One hundred cells were counted from three independent experiments and mean % senescent cells is noted in each micrograph.