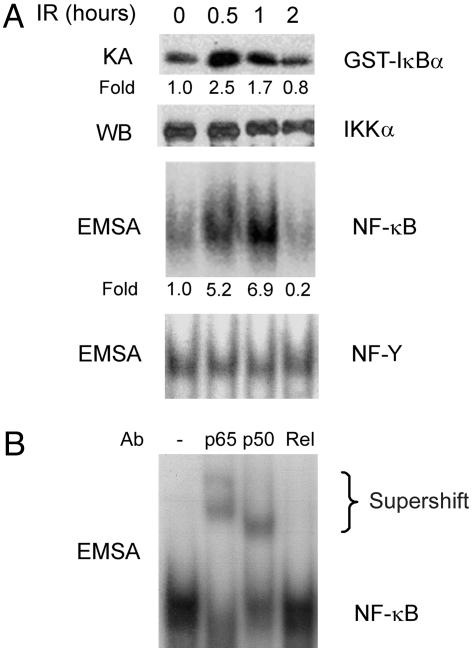
Fig. 1.
IR activates NF-κB in intestinal epithelial cells. (A) Mice were exposed to 8-Gy IR and, after the indicated times, epithelial cells were isolated from the mid-small intestine. IKK activity was determined by an in vitro kinase assay (KA), and IKKα levels were assessed as a loading control by Western blotting (WB). NF-κB binding activity was determined by electrophoretic mobility-shift assay (EMSA) with NF-Y binding activity used as a loading control. The fold induction of IKK and NF-κB activities in irradiated relative to nonirradiated mice are shown under each lane. (B) The components of the IR-induced NF-κB complex were investigated by supershift assay, using antibodies (Ab) against the indicated NF-κB proteins.