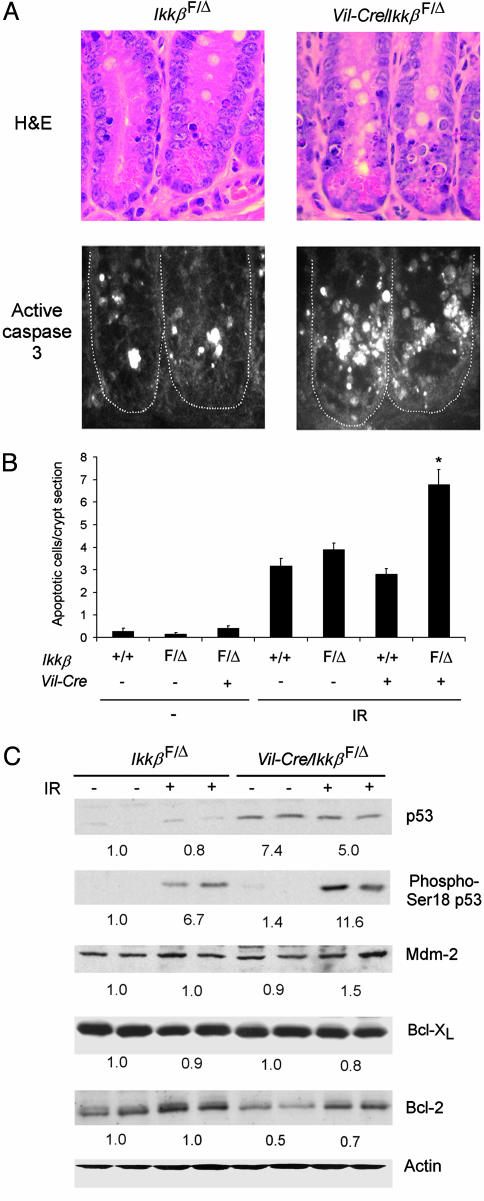
Fig. 3.
Increased apoptosis in small intestinal crypt epithelial cells of intestinal epithelial cell-specific IKKβ knockout mice. (A) Crypt epithelial cell morphology and caspase 3 activation in IkkβF/Δ and Vil-Cre/Ikkβ F/Δ mice after irradiation. Mice of the indicated genotypes were irradiated (8 Gy), and, after 4.5 h, sections of small intestine were prepared and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (Upper) or with anti-cleaved caspase-3 antibody (Lower). (B) Increased radiation-induced apoptosis in IKKβ-deficient intestinal epithelial cells. Mean (±SE) number of apoptotic cells per crypt section in the indicated nonirradiated mice (–, n = 4–8 mice per genotype) or in irradiated mice (IR, n = 9–16 mice per genotype). ANOVA, P < 0.0001; *, post hoc test, P < 0.01 compared to the three other genotypes exposed to IR. (C) Western blotting of protein extracts from small intestinal epithelial cells of IkkβF/Δ or Vil-Cre/IkkβF/Δ mice for p53, phosphoserine-18 p53, Mdm-2, Bcl-XL, Bcl-2, and actin. + indicates mice exposed to IR 4.5 h before cell isolation. Average relative protein abundance normalized to actin is shown beneath each pair of samples.