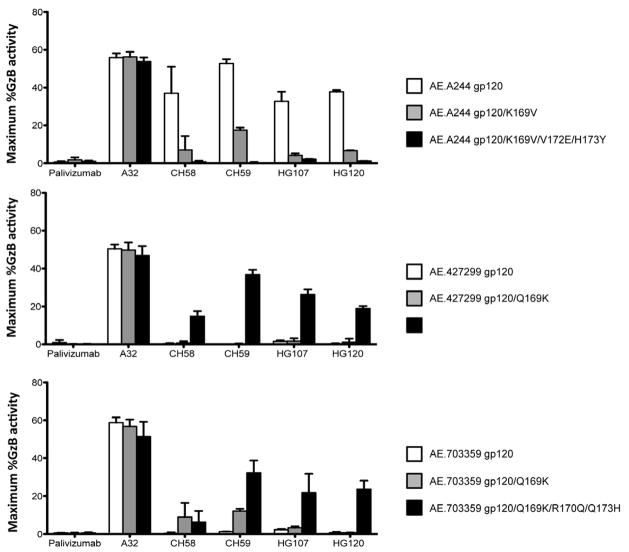
Figure 4. See also Figures S4 and S6. Effect of V2 mAbs CH58, CH59, HG107, HG120 footprint mutations in HIV-1 vaccine AE.A244 Env and RV144 breakthrough AE.427299 and AE.703357 Envs on ability of V2 mAbs to mediate ADCC.
Panels show the ability of mAb A32 and RV144 V2 mAbs CH58, CH59, HG107, HG120 to mediate ADCC against gp120-coated CD4 cell (CEMCCR5) target T cells. Data shown is maximum percent granzyme B activity from ADCC. Top panel shows that CH58, CH59, HG107 and HG120 mAbs all mediate high levels of ADCC against WT AE.244 Env coated CD4 T cell targets (white bars), and this killing is mitigated by a single K169V mutation (grey bars), and is abrogated by the full V2 mAb footprint set of mutations (black bars). Middle and lower panels show, in contrast, that none of the CH58, CH59, HG107 and HG120 mAbs mediated ADCC against RV144 breakthrough Env AE.427299 and AE.703357 WT CD4 T cell targets (with V2s that did not match the RV144 vaccine) (white bars), and that ADCC was restored minimally with AE.703357 targets with the Q169K mutation (grey bars), and restored in a pronounced manner in both breakthrough Env targets with the full set of mutations that include Q169K that restored the V2 mAb footprint mutations (black bars). Purified NK cells isolated from a normal donor with Fc-gamma receptor IIIα FF phenotype were used as effector cells. The effector to target ratio was 10:1. Error bars show mean +/− SEM. Each antibody was tested in a wide dose curve starting at 40ug/ml with 4-fold dilutions. See also Figures S6 and Table S5.