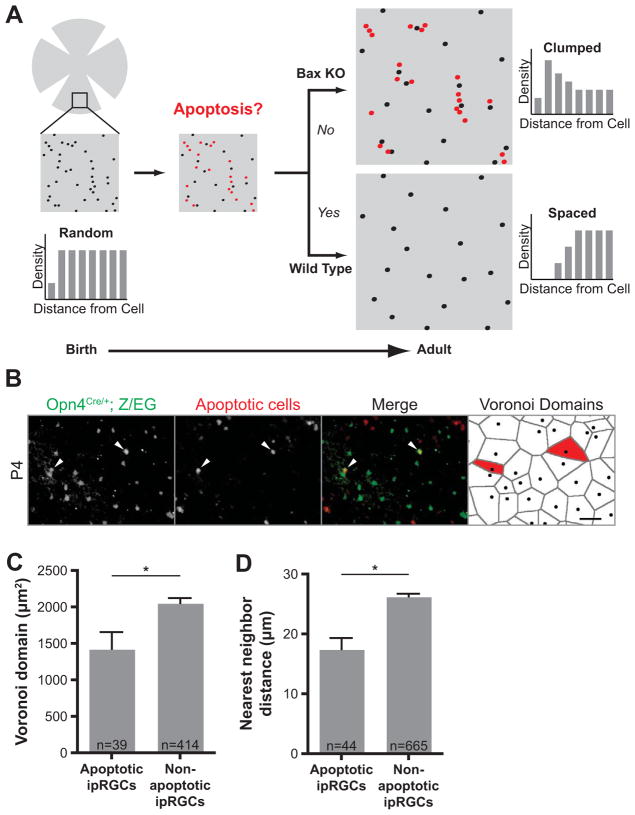
Figure 2. Proximity-based apoptosis leads to proper ipRGC spacing.
(A) Model showing how proximity-based apoptosis may generate a mosaic for a specific cell type. Only cell positioning, not fasciculation, is shown, for clarity. Cells in close proximity to each other (shown in red) are eliminated by Bax-mediated apoptosis to form a more spaced distribution in the adult. In Bax KO mice, cells in close proximity to each other survive. (B) Total ipRGCs were labeled in green at P4 with an anti-GFP antibody in Opn4Cre/+; Z/EG mice. Cells undergoing apoptosis were stained red by TUNEL and two antibodies specific for activated caspase-3 and activated Bax. Apoptotic ipRGCs (positive for any of these three indicators of cell death) are indicated with arrowheads (scale bar 50μm). The last panel shows Voronoi domains (VD) for each ipRGC in the field, with the VD for the dying ipRGCs labeled in red. (C) The subset of ipRGCs undergoing apoptosis at P4 have significantly smaller Voronoi domains than non-apoptotic ipRGCs (1429±230.5μm2, n=39 for apoptotic; 2059±66.95, n=414 for non-apoptotic, from eight retinas; p=0.0062 by Student t-test, Mean±SEM). (D) The apoptotic ipRGCs had a significantly smaller nearest neighbor distance to adjacent ipRGCs than non-apoptotic ones (17.49±1.848μm, n=44 for apoptotic; 26.28±0.4741μm, n=665 for non-apoptotic, from eight retinas; p<0.0001 by Student t-test, Mean±SEM).