Figure 1.
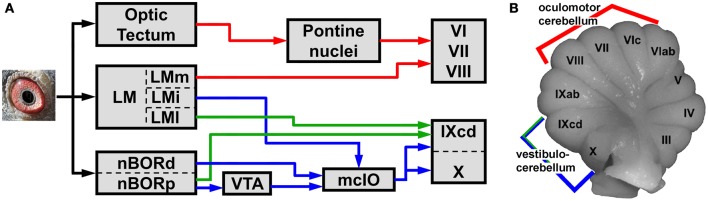
A reduced schematic, showing the visual pathways (A) to the cerebellum (B) in birds. The cerebellum is divided into folia, numbered I–X from anterior to posterior (Larsell, 1967). Folia IXcd and X comprise the vestibulocerebellum, which receives optic flow input from the nucleus of the basal optic root (nBOR) and lentiformis mesencephali (LM) via a climbing fiber pathway through the medial column of the inferior olive (mcIO) (blue pathway) (Arends and Voogd, 1989; Lau et al., 1998). The LM and nBOR also project directly to folium IXcd as mossy fibers (green pathways) (Brauth and Karten, 1977; Clarke, 1977; Brecha et al., 1980; Wylie and Linkenhoker, 1996). The LM also projects to folia VI–VIII (red pathway), which are part of the oculomotor cerebellum (Voogd and Barmack, 2006). These folia also receive visual motion signals from a tecto-pontine system (red pathway) (Reiner and Karten, 1982). See text for additional details. LMm, i, l: the medial, intercalatus, and lateral divisions of LM. nBORd, p: the dorsalis and proper divisions of nBOR. VTA: ventral tegmental area.
