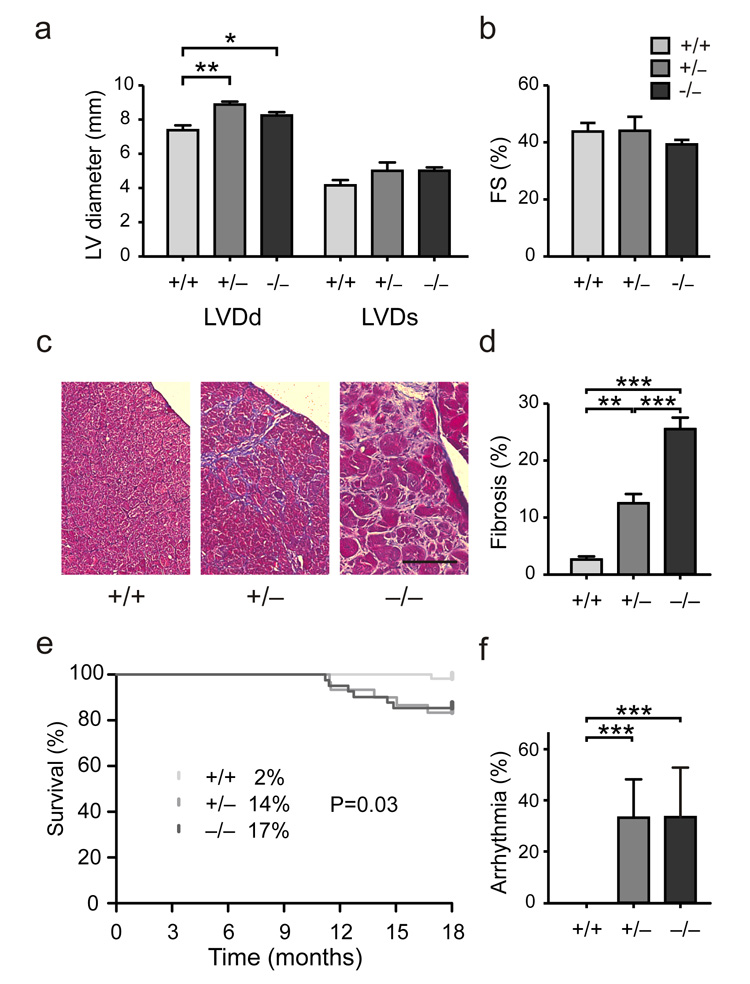
Figure 3.
Signs of cardiomyopathy with arrhythmia and sudden death in Rbm20 deficient rats. (a, b) Left ventricular diameter in diastole (LVDd) as determined by echocardiography was increased in both heterozygous and homozygous mutants as a sign of dilated cardiomyopathy (P < 0.05; n = 15). Changes in LV diameter in systole (LVDs) and fractional shortening (FS), a parameter of contractile function, did not reach statistical significance. (c) Subendocardial fibrosis was present in heterozygote mutants (+/−) as indicated by the trichrome staining (blue). The fibrotic area was increased and compacted in the homozygous hearts (−/−). Size bar = 100 μm. (d) Interstitial fibrosis was significantly increased in LV from heterozygous (13% fibrotic area) and homozygous (26%) as compared to wildtype hearts (3%). N = 13. (e, f) Increased inducibility of arrhythmia in both hetero- and homozygotes was associated with an increase in sudden death starting from 10 months of age. Deaths in percent are indicated at 18 months of age. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test P = 0.03; n = 130.