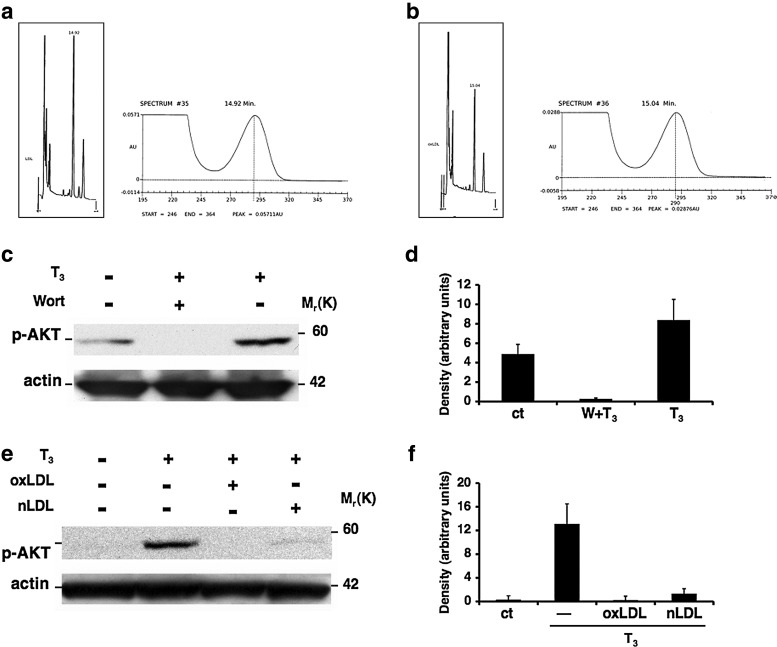
FIG. 2.
Inhibition of T3-mediated AKT phosphorylation by oxidized low-density lipoproteins (oxLDL). High-performance liquid chromatography of α-tocopherol content of LDL. Chromatogram of α-tocopherol content of native LDL (nLDL; non oxidized) corresponding to 48.46 μM (a); chromatogram of α-tocopherol content of LDL after one hour oxidation with 5 μM CuSO4 corresponding to 24.44 μM (b). Inhibition of AKT phosphorylation by LDL. HUVECs were treated with oxLDL or nLDL for 3 hours followed by T3 (10−7 M) treatment for 20 minutes. When indicated, cells were pretreated for 12 hours with vitamin E (150 μM) and vitamin C (150 μM). For the PI3K/AKT inhibition pathway, cells were pretreated with Wortmannin (10−7 M) for 30 minutes. A representative Western blot from three independent experiments shows the inhibition of T3-mediated AKT phosphorylation by (c) Wortmannin and by (e) oxLDL (50 μg/mL) and nLDL (50 μg/mL) compared with the T3 treatment. Quantification of bands was performed by densitometric analysis (d, f). Data are reported as mean±SD of three independent experiments.