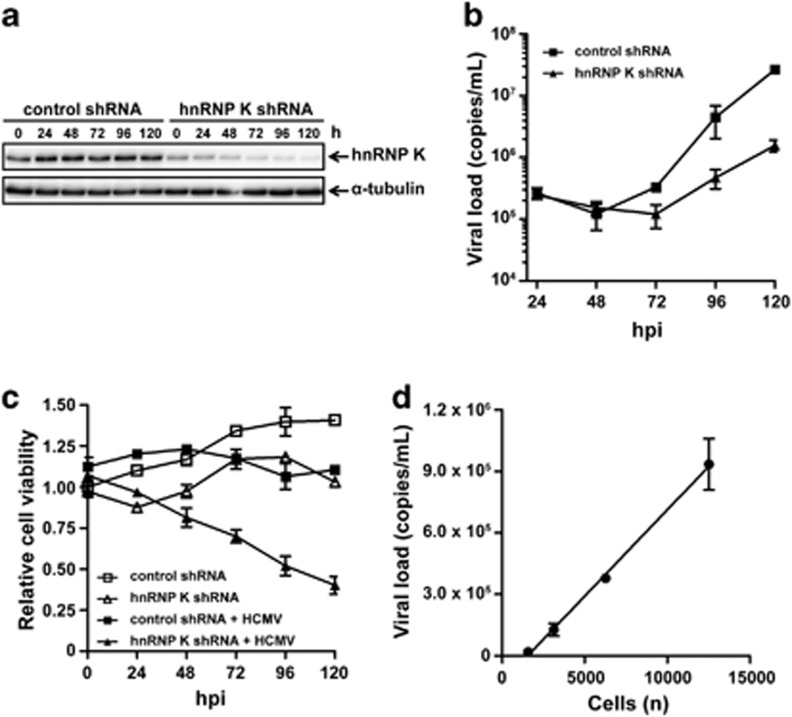
Figure 4.
HnRNP K is essential for HCMV replication. (a) HFFs were transduced with hnRNP K-specific or control shRNA and lysed at different time points. Lysates were subjected to immunoblotting using antibodies against hnRNP K or α-tubulin (loading control). (b) HnRNP K-deficient and control HFFs were infected with HCMV and viral load in supernatants at different time points was assessed by quantitative PCR. (c) Cell viability of uninfected or HCMV-infected transduced HFFs was determined by WST-1 assay and relative cell viability of uninfected control shRNA-treated cells at 0 h.p.i. was set to 1. (d) HFFs were seeded at different cell densities and infected with HCMV at a multiplicity of 1.0 plaque-forming unit per cell. Viral load in supernatants at 96 h.p.i. was assessed by quantitative PCR and a linear regression curve was plotted. Data depicted represent the mean±S.D. of triplicates