Figure 1.
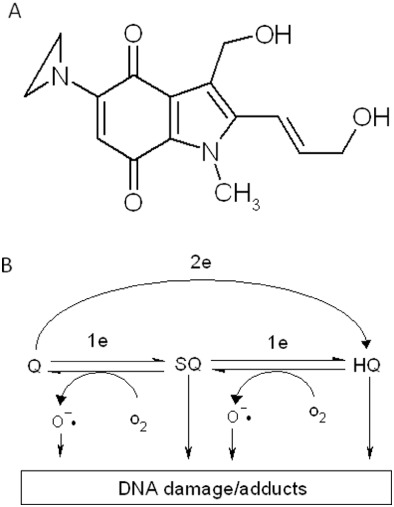
Chemical structure of EO9 (A) and scheme for possible activation of EO9 leading to DNA damage (B). 2e and 1e in panel B represent two-electron reduction (via enzymes such as NQO1) and one-electron reduction (via enzymes such as cytochrome P450 reductase) respectively. Q, SQ and HQ denote quinone (parent compound), semi-quinone (one-electron reduction product) and hydroquinone (two-electron reduction product) respectively.
