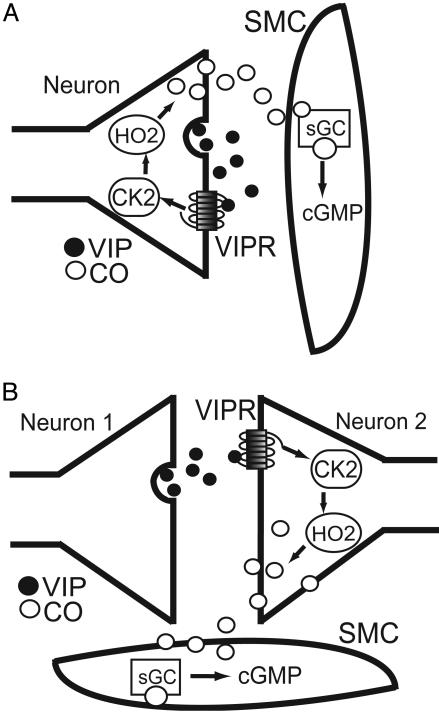
Fig. 6.
Mechanism of VIP-induced IAS relaxation. VIP is released from neurons within the IAS, where it can act on neurons and possibly smooth muscle cells (SMC). Neuronally localized HO2 participates either by means of autocrine (A) or paracrine (B) actions of VIP on neurons. Studies have shown that EFS-induced relaxation of IAS requires both HO2 and protein kinase CK2 activity (19). Therefore, we hypothesize that VIPR activation is linked to increases in CK2 activity (arrows), resulting in HO2 activation. Supporting this hypothesis, specific CK2 inhibitors block relaxant responses to exogenous VIP (C.C.W., D.B., C.D.F., A.I.K., and S.H.S., unpublished data). CO produced by HO2 diffuses to SMC, where it activates sGC and subsequent cGMP production, leading to SMC relaxation. •, VIP; ○, CO.