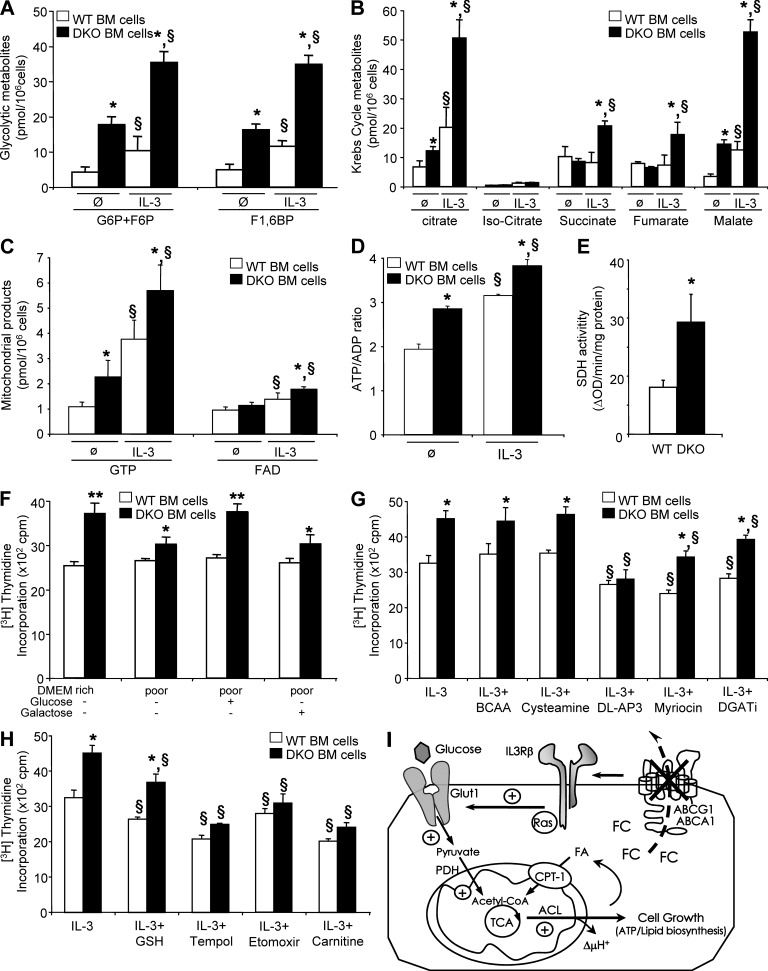
Figure 4.
The IL-3Rβ–dependent proliferation of Abca1−/−Abcg1−/− leukocytes is driven by increased mitochondrial metabolism. (A–D) Effect of IL-3 treatment on glycolytic metabolites (glucose 6-phosphate/fructose 6-phosphate and fructose 1,6-diphosphate; A), citric acid metabolites (B), related mitochondrial products (GTP and FAD; C), and ATP/ADP ratio (D) in WT and Abca1−/−Abcg1−/− BM cells determined by LC-MS. (E) SDH activity in these cells. Results are means ± SEM of cultures from three independent mice. *, P < 0.05 versus WT controls; §, P < 0.05 versus treatment. (F) WT and Abca1−/−Abcg1−/− BM cells were grown for 48 h in 20 mM glucose DMEM (DMEM rich) or low-glucose DMEM (DMEM poor) supplemented with 20 mM glucose or 20 mM galactose in the presence of IL-3. Proliferation rates were determined after 2-h [3H]thymidine pulse labeling. (G and H) BM cells were grown for 48 h in liquid culture containing 10% FBS IMDM in the presence of the indicated chemical compounds and IL-3. Proliferation rates were determined after 2-h [3H]thymidine pulse labeling. Results are means ± SEM of an experiment performed in triplicate. *, P < 0.05 versus WT controls; §, P < 0.05 versus untreated condition. BCAA, branched-chain amino acids; DGATi, diglyceride acyltransferase inhibitor. (I) Scheme illustrating the induction of glycolysis through modulation of plasma membrane cholesterol by ABCA1 and ABCG1 deficiency and increased mitochondrial metabolism that produces ATP and synthesizes lipids for cell growth. Lack of these transporters promotes growth factors dependent on IL-3Rβ signaling–mediated glycolysis as reflected by (a) enhanced Hk2 and PFKp mRNA expression, (b) enhanced glycolytic metabolites content, (c) enhanced glucose oxidation (i.e., conversion into CO2), and (d) reversal of enhanced glucose oxidation by removal of cellular cholesterol by cyclodextrin. The pyruvate generated through glycolysis is directed into the TCA cycle and increases mitochondrial metabolism as reflected by (a) enhanced mRNA expression of fumarase and SDHb, (b) enhanced SDH activity, (c) enhanced mitochondrial metabolites and mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔμH+), and (d) enhanced ATP/ADP ratio. Increased lipid synthesis was also observed in Abca1−/−Abcg1−/− BM cells as reflected by (a) enhanced mRNA expression of ACL and (b) enhanced glucose conversion into lipids.