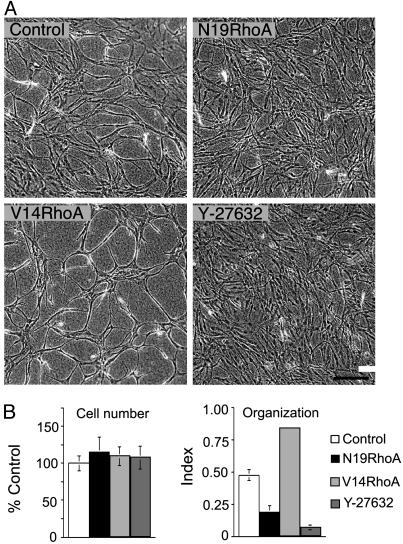
Fig. 4.
RhoA mutants regulate EC organization into precapillary cords. (A) Confluent EC monolayers, consisting of equal numbers of cells, were established on collagen I gels and, 24 h later, were overlaid with collagen I. Note that, relative to controls, dominant negative N19RhoA inhibited retraction and reorganization of confluent ECs into precapillary cords and that active V14RhoA promoted cord formation relative to controls. Similar to N19RhoA, the Rho kinase inhibitor (1 μM Y-27632, added at time 0) inhibited cord formation. (Bar = 200 μm). (B) Cell numbers were indistinguishable in the different experimental groups, but quantification of EC assembly into cords with morphometry indicated that organizational differences (see Materials and Methods) were highly significant (P < 0.001, error bars = standard deviations).