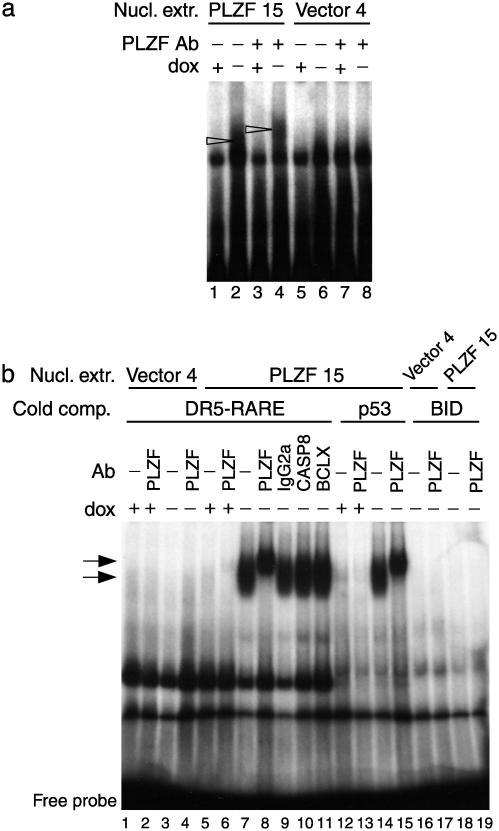
Fig. 4.
EMSA analysis using a sequence contained upstream of the BID TSS and nuclear extracts (Nucl. extr.) of the Jurkat clones PLZF 15 and vector 4. (a) EMSA using the BID radiolabeled probe without competitors. Arrowheads denote the presence of a retarded complex observed when nuclear extracts of clone PLZF 15 cultured in the absence of dox were used (lane 2) and the shifted complex when a PLZF mAb was used (lane 4). (b) EMSA using BID-radiolabeled probe with a 1,000-fold molar excess of unlabeled competitors (a DR5-RARE, lanes 1–11; a p53-binding site probe, lanes 12–15; or the specific unlabeled probe, lanes 16–19). Arrows denote the presence of a retarded complex observed when nuclear extracts of clone PLZF 15 cultured in the absence of dox were used (lanes 7, 9–11, and 14), and the shifted complex when a PLZF mAb was used (lanes 8 and 15). Irrelevant Abs failed to produce a shift (lanes 9–11). The complex was detected in the presence of a 1,000-fold molar excess of the irrelevant unlabeled competitors (lanes 7–11, 14, and 15), whereas it disappeared in the presence of the specific unlabeled probe (lanes 18 and 19).