Figure 2.
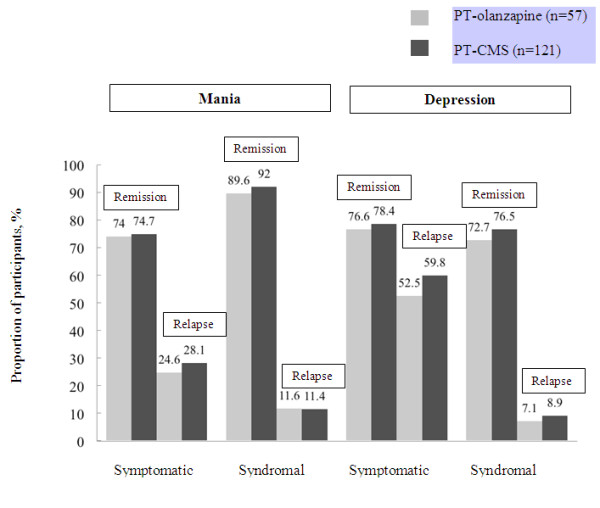
Proportion of Participants Experiencing Symptomatic1 or Syndromal2 Remission or Relapse into Mania or Depression. These are unadjusted data based on predominant treatment. Refer to Methods for the definitions of symptomatic relapse, symptomatic remission, syndromal relapse and syndromal remission for mania and depression. Groups were defined based on predominant treatment (PT; based on DDD units). PT-olanzapine refers to those participants (n = 57) in which olanzapine had the highest DDD unit value. PT-CMS refers to those participants (n = 121) in which a CMS had the highest DDD unit value. 1Symptomatic remission: from a manic state is defined as a YMRS total score of ≤12 and HAMD21 ≤8; from a depressive state is defined as a HAMD21 total score of ≤8. Symptomatic relapse: to a manic state, is based on a YMRS total score of ≥15 after having met the criteria for symptomatic remission (mania); to a depressed state is based on a HAMD21 total score of ≥15 after having met the criterion for symptomatic remission (depression). 2Syndromal remission: from a manic state is defined as all DSM-IV-TR ‘A’ and ‘B’ criteria for current manic episode are no worse than mild (≤3 on a 1 to 7 scale), and no more than two ‘B’ criteria are mild (=3 on a 1–7 scale); from a depressive state is defined as all DSM-IV-TR ‘A’ criteria for current major depressive episode are no worse than mild (≤3 on a 1–7 scale), and no more than three ‘A’ criteria are mild (=3 on a 1–7 scale). Syndromal relapse: to a manic state is based on meeting DSM-IV-TR criteria for current manic episode after having met the criteria for syndromal remission (mania); to a depressed state is based on meeting DSM-IV-TR criteria for current depressive episode after having met the criteria for syndromal remission (depression).
