Figure 5.
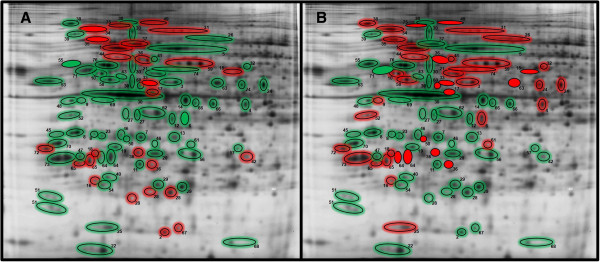
Sex differences in protein levels in KO and WT mice. Two identical reference gels (see also Additional file 2) are shown in Figure 5. Protein spots circled in green are expressed at lower levels in females and those with a red border are at higher levels in females. Significant changes are indicated by filled green or red circles. Panel A shows the male versus. female comparisons in KO mice and Panel B shows the differences in WT mice. The numbers adjacent to each spot indicate the protein and the names are listed below and correspond to those in Additional file 2: 1, 65-kDa macrophage protein; 2, Actin related protein 2/3 complex, subunit 5; 3, Actin-related protein 3; 4, Actr2 protein; 5, Alpha-fetoprotein; 6, Annexin A2; 7, Annexin A4; 8, Anxa5 protein; 9, ArsA arsenite transporter, ATP-binding, homolog 1; 10, Atp5b protein; 11, Calpain, small subunit 1; 12, Capping protein (actin filament) muscle Z-line, alpha 2; 13, Capping protein (actin filament) muscle Z-line, beta isoform a; 14, Cathepsin D precursor; 15, Chaperonin subunit 2 (beta); 16, Chia protein; 17, Chitinase 3-like 3 precursor; 18, Chitinase-related protein MCRP; 19, Chloride intracellular channel 1; 20, Chloride intracellular channel 4; 21, CNDP dipeptidase 2; 22, Coactosin-like 1; 23, EF hand domain containing 2; 24, Eno1 protein (Alpha-enolase); 25, Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A; 26, Ezrin; 27, F-actin capping protein alpha-1 subunit; 28, Ferritin heavy chain 1; 29, Ferritin light chain 1; 30, Gamma-actin; 31, Gelsolin precursor; 32, Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase X-linked; 33, Guanine deaminase; 34, Heat shock protein 1, beta; 35, Heat shock protein 5 precursor; 36, Heat shock protein 65; 37, Heat shock protein 8; 38, Heat shock protein 90, beta (Grp94), member 1; 39, Hematopoietic cell specific Lyn substrate 1; 40, Heme-binding protein; 41, Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K; 42, High mobility group 1 protein; 43, Hnrpf protein; 44, Kappa-B motif-binding phosphoprotein; 45, Keratin complex 2, basic, gene 8; 46, Keratin type II; 47, Krt13 protein; 48, Laminin receptor; 49, Major vault protein (MVP); 50, Microtubule-associated protein, RP/EB family, member 1; 51, Myosin light chain, regulatory B-like; 52, Nucleophosmin 1; 53, p50b; 54, Peroxiredoxin 2; 55, Prolyl 4-hydroxylase, beta polypeptide precursor; 56, Proteasome (prosome, macropain) 28 subunit, alpha; 57, Proteasome alpha 1 subunit; 58, Protein disulfide isomerase associated 6; 59, Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 precursor; 60, Protein synthesis initiation factor 4A; 61, Purine nucleoside phosphorylase; 62, Put. beta-actin (aa 27–375); 63, Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta; 64, Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) alpha; 65, Rho, GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) beta; 66, Serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade B, member 1a; 67, Stathmin; 68, Superoxide dismutase 1, soluble; 69, Superoxide dismutase 1, soluble; 70, Tropomyosin 3, gamma; 71, Tubulin, beta 5; 72, Tyrosine 3/tryptophan 5 -monooxygenase activation protein, epsilon polypeptide; 73, Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, beta polypeptide; 74, Vacuolar adenosine triphosphatase subunit B; 75, Valosin-containing protein; 76, Vimentin.
