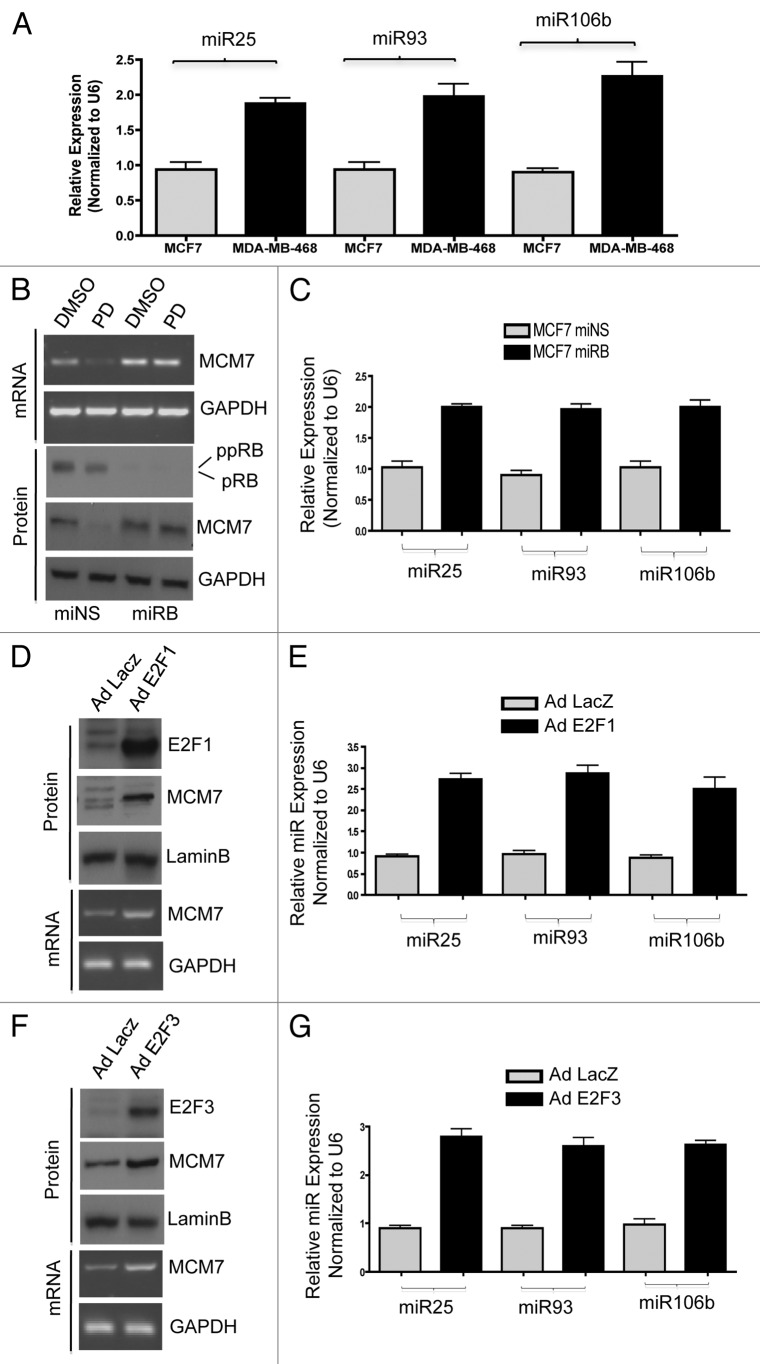
Figure 4. Comparative analysis of miR106b cluster expression in different breast cancer cell lines in response to PD 0332991 and RB status. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of miR106b cluster in RB-proficient MCF7, RB mutant MDA-MB 468 cells and the signals are normalized to U6 internal control. (B) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of MCM7 mRNA and loading control GAPDH in miNS and miRB MCF7 cells (top panel) and immunoblot analysis of pRB, MCM7 and loading control lamin b (bottom panel). (C) qRT-PCR analysis of miR106b cluster in miNS and miRB MCF7 cells, and the signals are normalized to U6 internal control. (D) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of MCM7 and GAPDH mRNA in E2F1-overexpressing MCM7 cells (bottom panel) and immunoblot analysis of MCM7, E2F1 and lamin b in E2F1-overexpressing MCM7 cells (top panel). (E) qRT-PCR analysis of miR106b- cluster in E2F1-overexpressing MCF7 cells and the signals are normalized to U6 internal control. (F) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of MCM7 and GAPDH mRNA (bottom panel) and immunoblot analysis of MCM7, E2F3 and lamin b in E2F3-overexpressing MCM7 cells (top panel). (G) qRT-PCR analysis of miR106b cluster in E2F3-overexpressing MCF7 cells and the signals are normalized to U6 internal control. Each data point is a mean ± SD from three or more independent experiments. p < 0.05 were considered as significant.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.