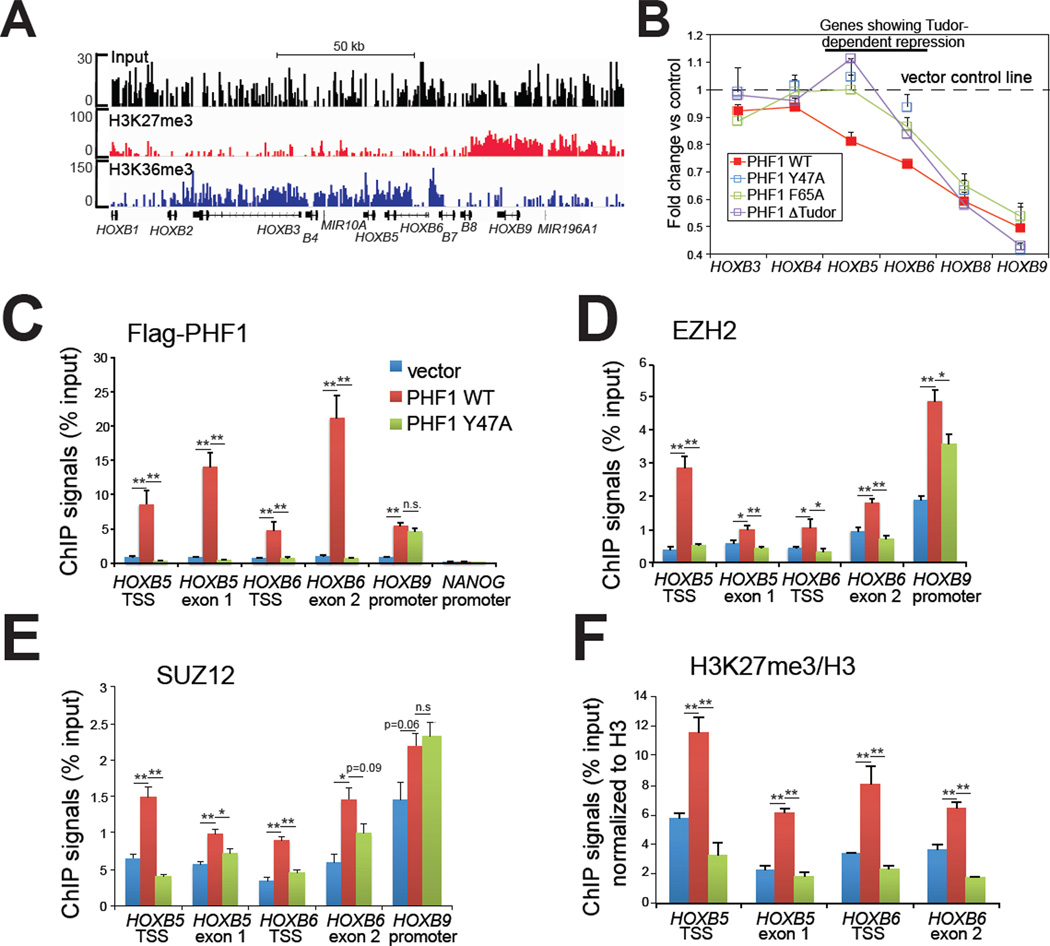
Figure 4. Ectopic expression of PHF1 induced a Tudor-dependent spreading of PRC2 complexes and H3K27me3 into an adjacent H3K36me3 region within HOX-B gene clusters.
(A) ChIP-Seq revealing a bimodal distribution of H3K27me3 and H3K36me3 at HOX-B gene clusters. Position of each HOX is indicated at the bottom. See also Figure S4.
(B) Change in expression of HOX-B genes in HeLa stable cells with ectopic expression of either wild-type or Tudor-mutant form of PHF1. Overexpression of the wild-type, but not Tudor-mutant form of PHF1 led to repression of HOXB5, and HOXB6 (highlighted by a line on the top), two genes situated at the H3K36me3-H3K27me3 conjunction (panel A). Data of relative mRNA levels (y axis) from three independent experiments were normalized against vector control (shown as a dash line), and then presented as mean ± SD.
(C–F) ChIP for FLAG-tagged PHF1 (C), EZH2 (D), SUZ12 (E) and H3K27me3 (F) across different HOX-B genes in HeLa cells overexpressing either wild-type PHF1 or its Tudormutant form. Data of ChIP signals (y axis) from three independent experiments were normalized to 1% of input used, data of histone modification (F) further normalized to those of total histone H3, and then presented as mean ± SD. Statistics shown are t-test comparisons of ChIP in cells transduced with wild-type (WT) PHF1 to that with control or the mutant (Y47A) form. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.005; n.s., not significant.