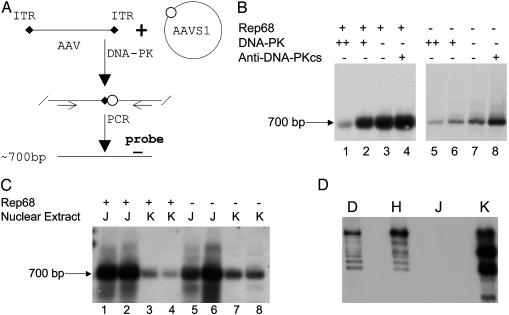
Fig. 1.
DNA-PK inhibits AAV integration in vitro. (A) Schematic diagram of the in vitro integration assay for testing the roles of the DNA-PK. (B) In vitro integration assays were performed with or without DNA-PK (200 units for lanes 1 and 5; 20 units for lanes 2 and 6) or antibody against DNA-PKcs (0.4 μg for lanes 4 and 8). HeLa nuclear extract was used in all reactions. The integration reactions were stopped and heated at 94°C for 10 min before PCR. When the integration reactions were performed with Rep68, half the amount of the reaction products was used as PCR template (lanes 1-4) to avoid saturation of the PCR and to evaluate the effects of DNA-PK and the anti-DNA-PKcs. When the integration reactions were performed without Rep68, the total reaction product was used as PCR template for enhancing amplification of the junction. An ≈700-bp PCR amplified junction (as indicated) of AAV and the AAVS1 site was detected by Southern blot with AAVS1 probe. (C) In vitro integration assay using nuclear extracts from DNA-PKcs-negative cells, M059J (J), and NDA-PKcs-positive cells, M059K (K). No HeLa nuclear extract was added in these reactions. (D) Western blot for DNA-PKcs. Antibody (Ab1, NeoMarkers, Fremont, CA) was diluted (1:200) and used to detect DNA-PKcs in the nuclear extracts from HeLa (H), M059J (J), and M059K (K) cells. DNA-PK (D) from Promega was used for positive control.