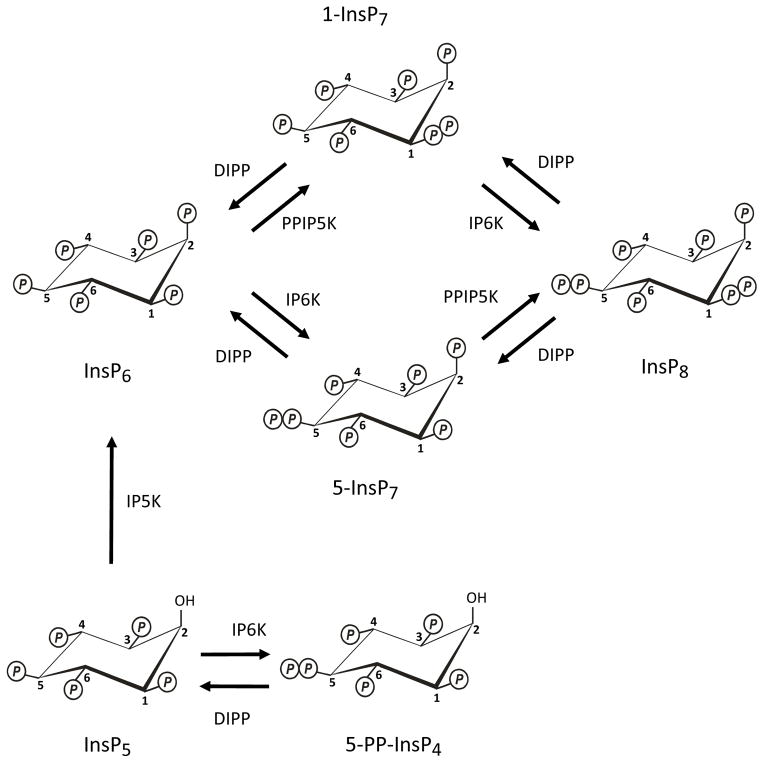
Fig. 1. Synthesis and metabolism of the PP-InsPs.
The figure describes the metabolic reactions that account for the turnover of the P-InsPs in both yeasts and mammalian cells. The positions of the diphosphate groups were determined in the following publications: (Albert et al., 1997; Draskovic et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2012). DIPP (E.C. 3.6.1.52; Ddp1 in yeast), diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase; IP5K (E.C. 2.7.1.158; Ipk1 in yeast), inositol pentakisphosphate kinase; IP6K (E.C.2.7.4.21; Kcs1 in yeast), inositol hexakisphosphate kinase, PPIP5K (E.C.2.7.4.24; Vip1 in yeast), diphosphoinositol pentakisphophate kinase.