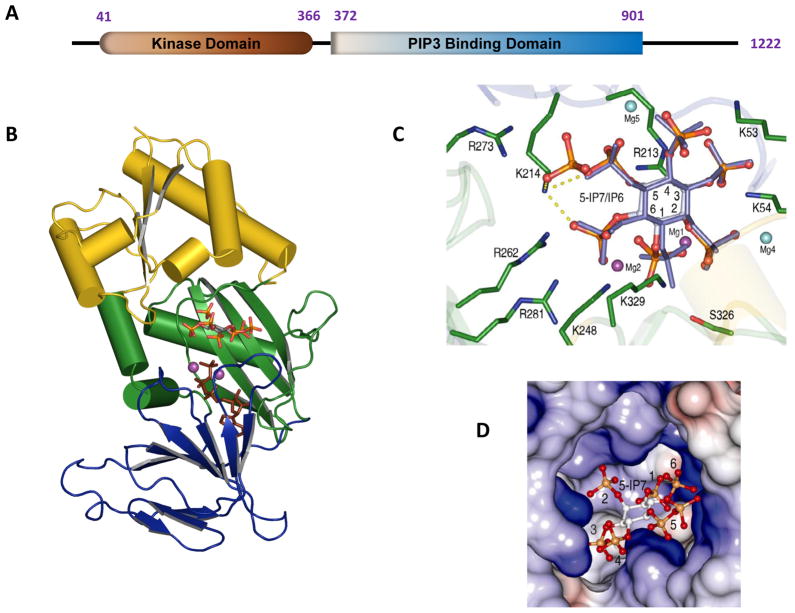
Fig. 2. Structure of the kinase domain of human PPIP5K2.
A is a graphical depiction of the modular format of PPIP5K2; the numbering of the amino acid residues depicts where the domains are considered to begin and finish. B, Ribbon diagram of residues 37-366 of PPIP5K2KD. The αβα domain (residues 42–124 and 330–366) is shown in yellow. The two antiparallel β-sheet clusters of the ATP-grasp domain are colored green (residues 125–148 and 244–329) and blue (residues 149–243). Shown in stick models are 5-InsP7 and AMP-PNP. C, Active site of PPIP5K2 KD. Shown in green are residues that make polar contacts with substrates. 5-InsP7 is shown with grey carbon and orange and red phosphate groups, while InsP6 is slate-colored. Carbon atoms on the inositol ring are numbered. The interactions of Lys214 with 5-InsP7 are highlighted by dashed yellow lines. The sky blue and purple spheres represent the magnesium atoms; The purple magnesium atomss (Mg1 and Mg2) were catalytically relevant. Mg5 was not present in the PPIP5K2KD–InsP6 complex. See (Wang et al., 2012) for full details. D, Electrostatic surface representation of the inositol phosphate substrate binding pocket of PPIP5K2KD.