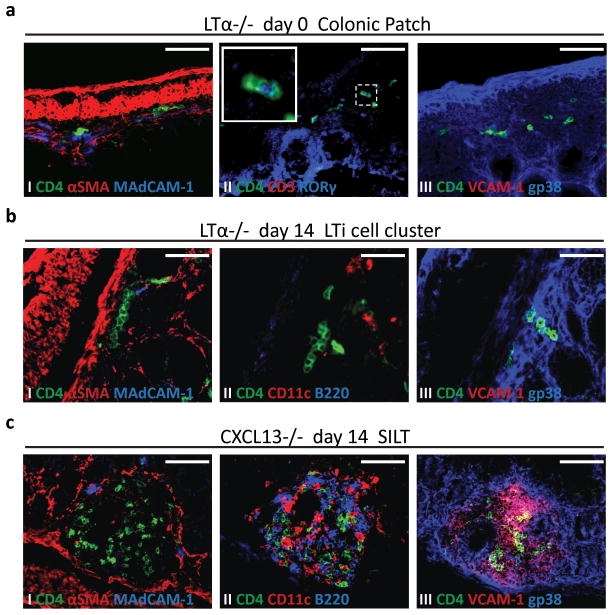
Figure 3. Lymphotoxin and CXCL13 are both required for colonic patch development, but only lymphotoxin, and not CXCL13, is required for colonic SILT formation.
a Immunofluorescence characterization of colonic patch anlagen present in LTα−/− mice at day 0 post-partum, stained for (I) CD4 (green), αSMA (red), and MAdCAM-1 (blue), (II) CD4 (green), CD3 (red), and RORγ (blue) (insert is a higher magnification of LTi cells expressing RORγ), and (III) CD4 (green), VCAM-1 (red), and gp38 (blue). b,c Immunoflourescence characterization of lamina propria lymphoid aggregates present in the colon of LTα−/− (b) and CXCL13−/− (c) mice at day 14 post-partum, stained for (I) CD4 (green), αSMA (red), and MAdCAM-1 (blue), (II) CD4 (green), CD11c (red), and B220 (blue), and (III) CD4 (green), VCAM-1 (red), and gp38 (blue). Scale bars 50μm. At least 3 colons per group were entirely sectioned and the detected lymphoid tissues further analyzed.