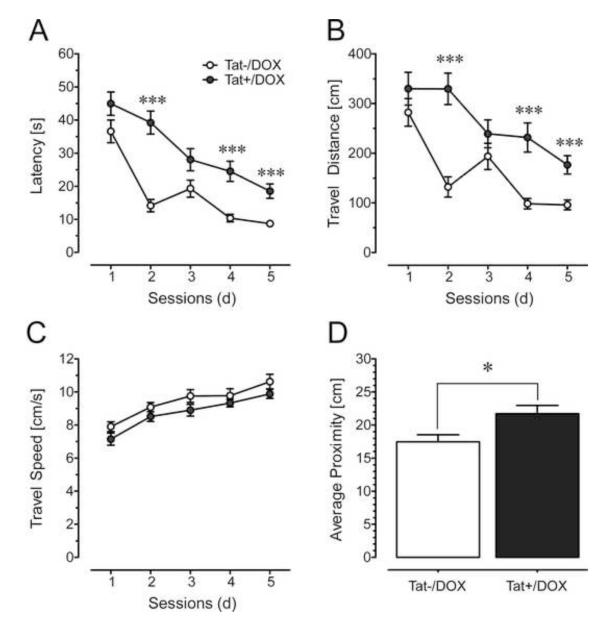
Figure 5.
Effects of Tat induction in the Morris water maze in acquisition training across session (A-C) and the probe test (D) for 2-3-mo old mice (mean ± SEM). (A-C) Two-way mixed ANOVAs were conducted with Tat induction as a between-subjects factor (2 levels) and session number (the data from 4 trials within each session were combined) as a within-subjects factor (5 levels). (A) Escape latency is increased for Tat+/DOX mice (n = 9) [main effect of Tat: F(1, 16) = 49.47, p < 0.001], indicating longer search times for Tat+/DOX mice to find the hidden platform compared to the control (Tat−/DOX, n = 9) mice. Post hoc tests conducted for each session reveal significant differences between the two groups for sessions 2, 4 and 5. There is also a learning effect across session for both groups expressed in a significant main effect of time [F(4, 64) = 25.84, pGG < 0.001]. A Tat induction x session interaction [F(4, 64) = 2.88, pGG < 0.05] indicates that with time, Tat−/DOX mice learn to find the hidden platform more rapidly than transgenic mice following Tat induction (Tat+/DOX). (B) Travel distance is increased for Tat+/DOX mice [main effect of Tat: F(1, 16) = 36.02, p < 0.001], with post hoc tests indicating that Tat+/DOX mice routinely swim longer distances before finding the platform for all sessions except at 3 d. There is also a learning effect across session for both groups [F(4, 64) = 13.39, pGG < 0.001] as well as a significant Tat induction x session interaction [F(4, 64) = 3.32, pGG < 0.05]. (C) Travel speed (cm/s) indicated a modest effect in the ANOVA for Tat induction [F(1, 16) = 6.38, p < 0.05] that however did not hold up in post hoc tests. Further, a significant session effect was noted, with both groups swimming faster across session [F(4, 64) = 14.26, pGG < 0.001]. No Tat induction x session interaction was noted. (D) For the probe test, conducted 2 d after the last acquisition session, a one-way ANOVA was conducted with Tat induction as a between-subjects factor (2 levels). The proximity index (cm) indicated that control mice swim more closely to the previous location of the platform compared to the Tat+/DOX mice [Tat induction effect: F(1, 15) = 6.54, p < 0.05]. ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05; DOX: doxycycline.