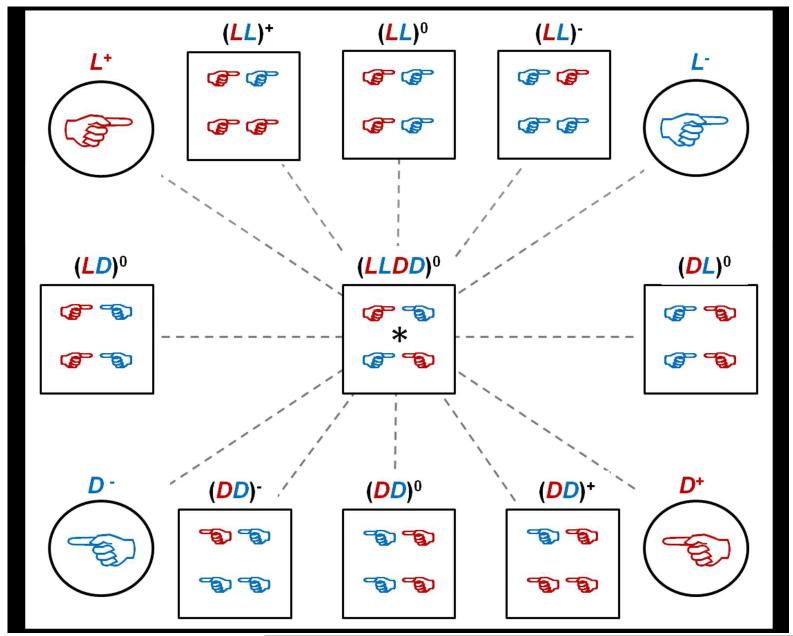
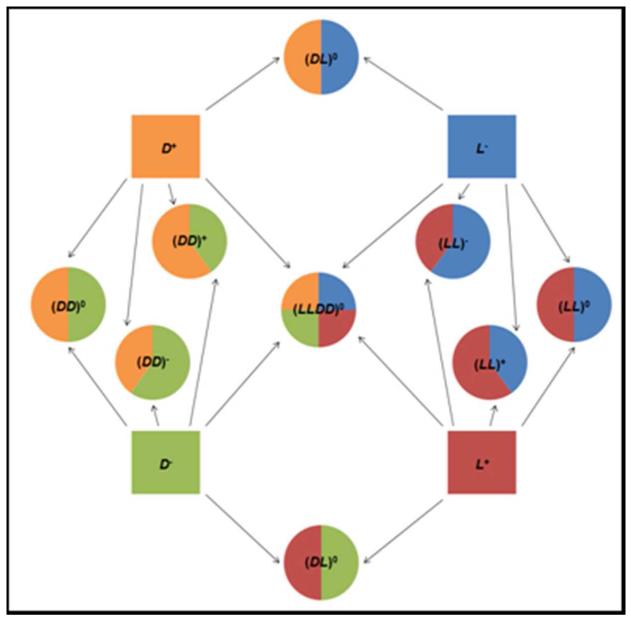
Figure 1.
(A) Pictorial description of the 4 parent solutions and 9 hydrogel types made. The dashed lines connect mirror images which all run through (LLDD)0, which is its own mirror image. Red hands represent positively charged peptides and blue hands represent negatively charged peptides. Circles represent the parent oligopeptide solutions used to make the hydrogels. Squares represent the hydrogels. (B) Pictorial description of how each gel was made using different amounts of four parent oligopeptides. The final oligopeptide concentration for all gels was 5 mM. Neutral gels were made with 2.5 mM D+ or L+ and 2.5 mM D− or L−; positively charged gels were made with 3 mM D+ or L+ and 2 mM D− or L−; and negatively charged gels were made with 2 mM D+ or L+ and 3 mM D− or L−.