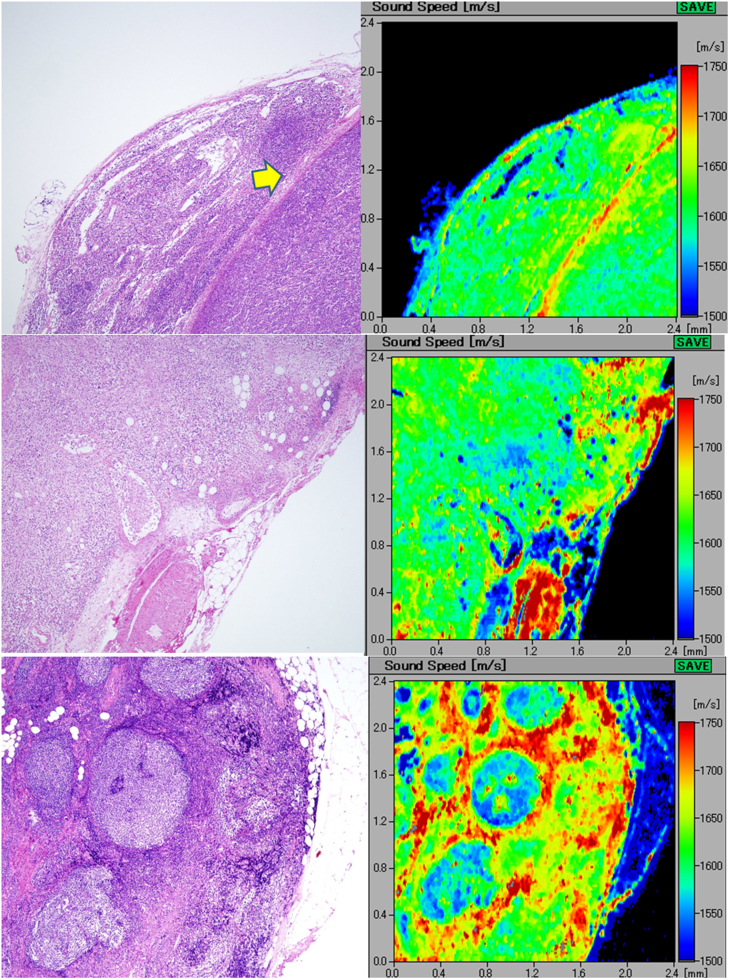
Figure 4.
A(upper) Diffuse, large B-cell lymphoma. the lymph node loses normal architecture and is replaced by dense monotonous lymphoma cells (left; H&E stain). The scanning acoustic microscopy image (right) shows homogenous structure with rather high speed of sound values. The lymphoma penetrates through the fibrous capsule (arrow) into the adjacent connective tissue. B(middle) Hodgkin lymphoma. the lymphoma cells densely infiltrate into the lymph or blood vessels and the outer adipose tissue. The invasive area of the lymphoma exhibits a homogenous higher speed of sound area. The slower speed spots within the lymphoma in the scanning acoustic microscopy image correspond to the residual fat cells. C(lower) Follicular lymphoma extending into the extracapsular adipose tissue. the lymph node is replaced by nodular lymphoma cells. In the right scanning acoustic microscopy image, nodular structures with lower speed of sound (SOS) values are surrounded by the lymphoma cell-rich mantles with higher SOS values.