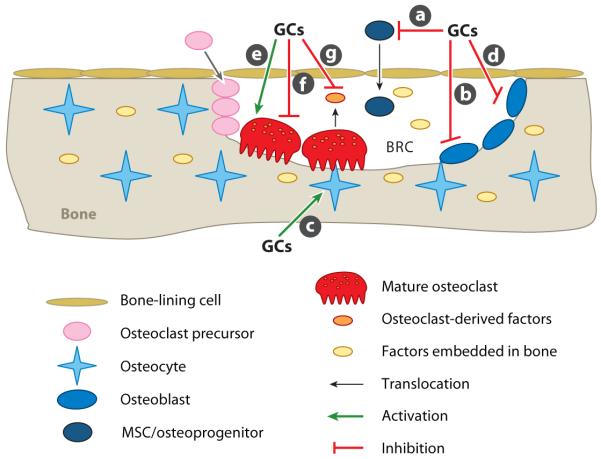
Figure 4.
Current understanding of the pathological mechanisms of glucocorticoid (GC)-induced osteoporosis. (a) Inhibition of differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and osteoprogenitors into osteoblasts. (b) Impairment of osteoblast function and enhancement of osteoblast apoptosis. (c) Induction of apoptosis of osteocytes. (d) Enhancement of receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand and reduction of osteoprotegerin expression in osteoblasts. (e) Prolonging of the life span of osteoclasts. (f) Inhibition of osteoclast function. (g) Suppression of osteoclast-generated osteogenic factors. Abbreviation: BRC, bone-remodeling compartment.