Fig 1.
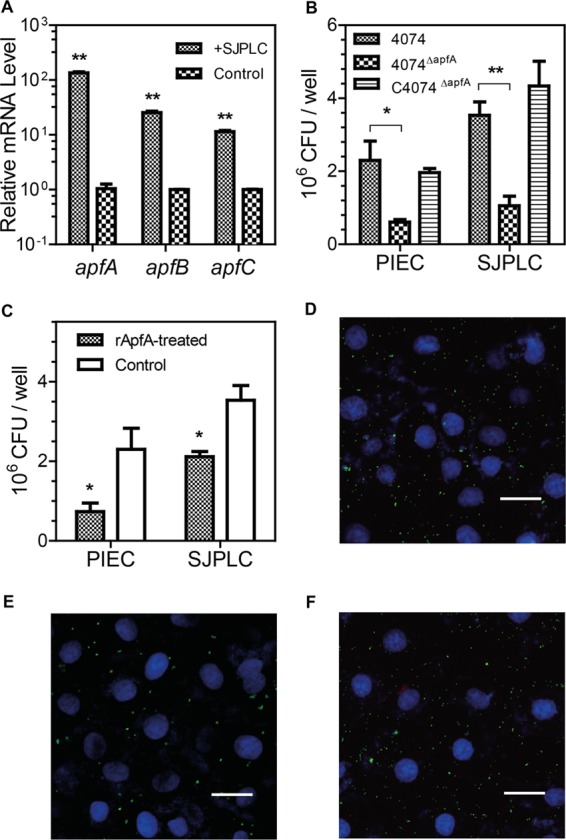
The expression of type IV fimbriae is induced upon contact with host cells, and ApfA mediates the adhesion of A. pleuropneumoniae to host cells. (A) The relative mRNA levels of the apfA, apfB, and apfC genes were upregulated after A. pleuropneumoniae 4074 was cocultured with SJPL cells (SJPLC), compared to those of bacteria without cell coculture. The mRNA level was determined by qRT-PCR. (B) Adhesion capabilities of wt strain 4074, mutant strain 4074ΔapfA, and complementary strain C4074ΔapfA to SJPL and PIEC cells. (C) Blockage of A. pleuropneumoniae adhesion to SJPL and PIEC cells by rApfA. SJPL and PIEC cells were pretreated with rApfA (rApfA-treated) or BSA (Control) before being subjected to contact with bacteria. The data shown are means ± SD of data determined with triplicate samples of one experiment representative of three independent experiments. The asterisks show significant differences (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). Confocal microscopy showed the adhesion of wt strain 4074 (D), mutant strain 4074ΔapfA (E), and complementary strain C4074ΔapfA (F) to SJPL cells. A. pleuropneumoniae cells were labeled with CFDA (green fluorescence). SJPL cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue fluorescence) (scale bars = 50 μm).
