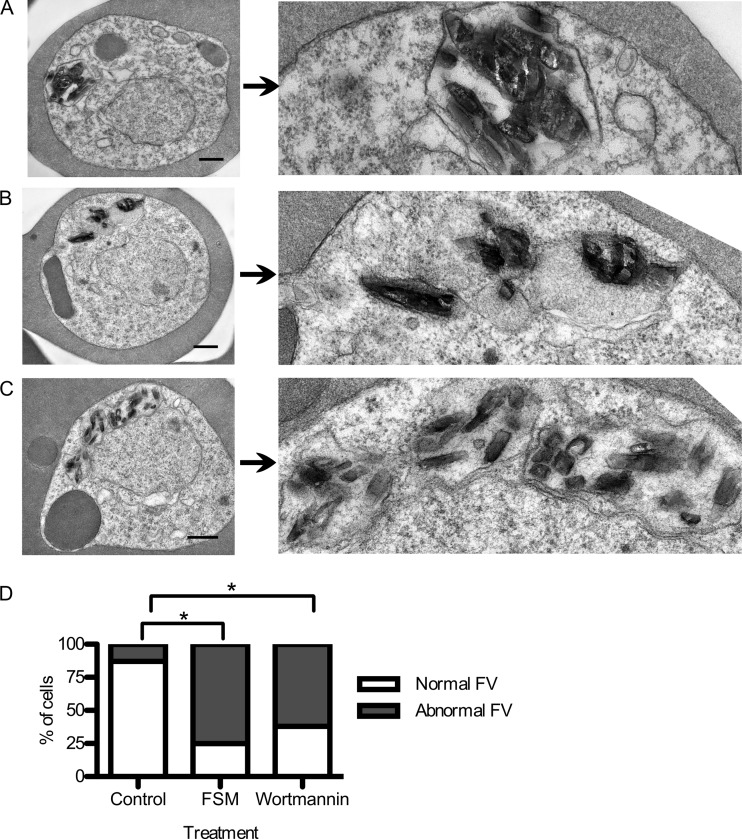
Fig 6.
Food vacuolar defect in fosmidomycin- and wortmannin-treated parasites. (A to C) Transmission electron microscopic evaluation of control parasites (A) compared to parasites treated for 24 h with either the isoprenoid inhibitor fosmidomycin (B) or the PI3-K inhibitor wortmannin (C). On the right is a magnified view of a hemozoin-containing FV. (D) Scoring of electron micrographs of control versus fosmidomycin (FSM)- and wortmannin-treated cells. Abnormal FVs were defined as FVs that either lacked an FV membrane or contained more than one discontiguous membrane-bound collection of hemozoin (n > 25 under each condition). ∗, P < 0.001 compared to untreated conditions (Fisher's 2-tailed test).