Fig 8.
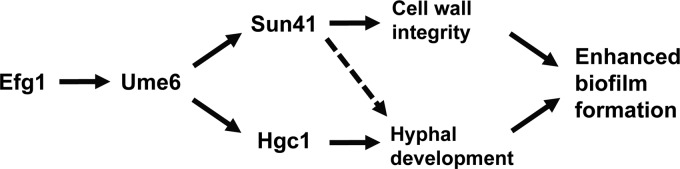
Model for roles of Efg1, Hgc1, and Sun41 in UME6-driven enhanced C. albicans biofilm formation. Ume6 functions downstream of Efg1 and upstream of both Hgc1 and Sun41 to promote biofilm development. UME6 expression is known to cause transcriptional induction of the Hgc1 cyclin-related protein, which, in turn, directs hyphal development via septin phosphorylation, inhibition of cell separation genes, and activation of the Cdc42 master polarity regulator (38–44). UME6 expression also appears to cause a slight increase in SUN41 transcript levels. SUN41, in turn, may function indirectly in a positive-feedback loop to increase UME6 expression levels (not shown); however, the relevance of these transcriptional effects for biofilm formation has not yet been established. In either case, Sun41, a putative cell wall glycosidase, is known to be primarily involved in maintaining cell wall integrity (27). Both the physical process of hyphal development and Sun41-mediated cell wall integrity therefore appear to play important roles in UME6-driven enhanced biofilm formation. In addition, we cannot exclude the possibility that Sun41 at least partly contributes to UME6-driven biofilm growth by playing a role in hyphal development (dashed line). Finally, it is important to note that an additional mechanism(s), which at this point has not yet been determined, may also contribute to UME6-driven enhanced biofilm formation.
