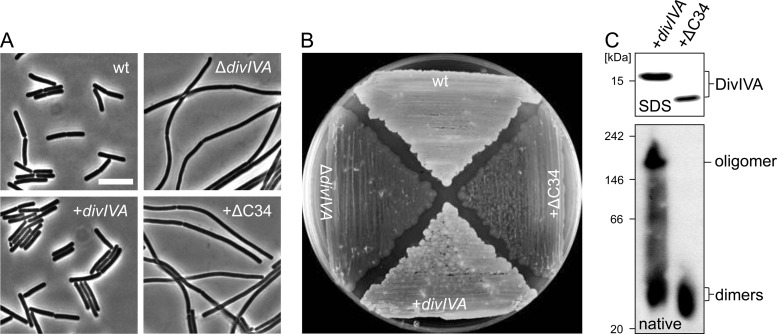
Fig 2.
Complementation activity and oligomerization of a C-terminally truncated DivIVA protein devoid of the tetramerization domain. (A) Phase-contrast micrographs showing cellular morphology of strain BSN360 expressing the DivIVAΔC34 protein. Cultures of strain 168 (wt), strain 4041 (ΔdivIVA), and the complemented ΔdivIVA mutant strain BSN356 (+divIVA) were included as controls. Cells were cultivated in LB broth (containing 1 mM IPTG where necessary) to mid-logarithmic growth phase at 37°C before images were taken. Bar, 5 μm. (B) Sporulation of the same set of strains on Schaeffer's sporulation agar containing 1 mM IPTG. Cells were kept for 3 days at 37°C until lysis of the Spo− strains became apparent. (C) Western blots after SDS-PAGE and blue native PAGE to analyze expression and oligomerization of DivIVAΔC34. Strains BSN356 (+divIVA) and BSN360 (+ΔC34) were cultivated as described above, and cellular protein extracts were subjected to SDS-PAGE (top) or blue native PAGE (bottom) and subsequent Western blotting. DivIVA was detected using the polyclonal anti-DivIVA antiserum. The NativeMark standard (Invitrogen) was used as a molecular mass marker for blue native PAGE.