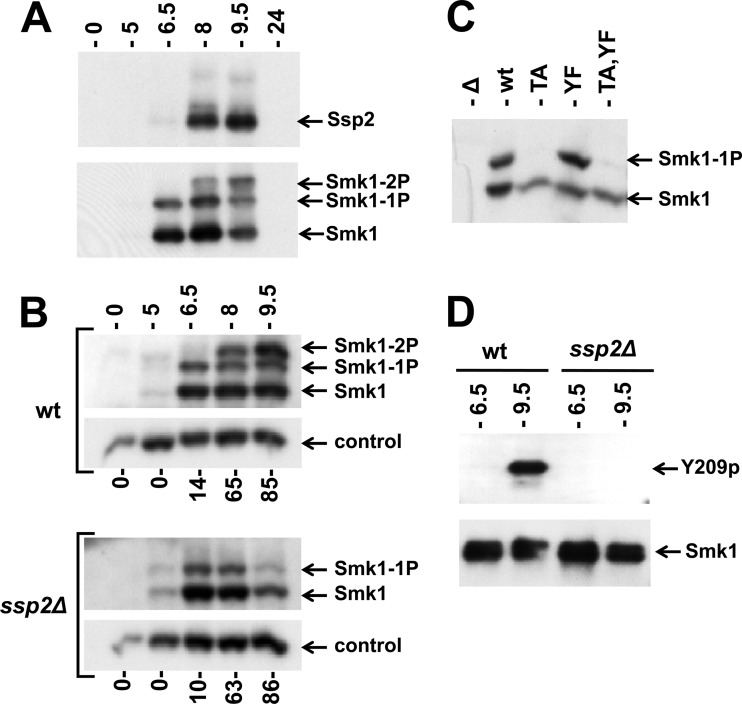
Fig 3.
Phosphorylation of Smk1 on Y209 requires Ssp2. (A) Extracts from meiotic cells were prepared at the indicated times postinduction and analyzed by electrophoresis through Phos-tag gels and immunoblotting. A single filter was sequentially analyzed using anti-Myc (upper panel; Ssp2) or anti-HA (lower panel; Smk1) antibodies. (B) Sporulation was induced in wild-type (wt) and ssp2Δ strains as indicated, and Smk1-HA was analyzed as described for panel A. Cdk1 (Cdc28), which is present at a constant level throughout sporulation, was monitored using a PSTAIR antibody as a loading control. The fraction of cells that had completed MII at each time point is indicated below the immunoblots (n = 100). (C) smk1Δ ssp2Δ strains harboring low-copy-number (CEN-based) Smk1-HA plasmids with the indicated activation loop mutations (TA, T207A; YF, Y209F) were collected 9.5 h following transfer to sporulation medium, and Smk1-HA was analyzed as described for panel A. (D) Smk1-HH proteins were purified from wild-type and ssp2Δ meiotic cells collected 6.5 h and 9.5 h after transfer to sporulation medium. Comparable amounts of Smk1-HH were resolved by electrophoresis in gels lacking Phos-tag and analyzed by immunoblotting using phosphospecific Y209p peptide antisera (Y209p) or an anti-HA antibody (Smk1).