Fig 2.
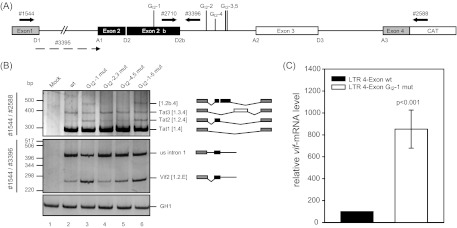
Alternative 5′ss within HIV-1 NL4-3 intron 2 leads to alternative transcript isoforms. (A) Schematic drawing of the HIV-1 pNL4-3-derived subgenomic splicing reporter (LTR 4 exon). The reporter contains noncoding leader exons 2 and 3 flanked by authentic NL4-3 sequences. Coding regions for gag and pol in intron 1 have been deleted and replaced with a shorter linker sequence (see Materials and Methods). The 5′ss and 3′ss, including D2b, are indicated. The positions of the RT-PCR primers used are depicted by arrows. (B) RT-PCR analysis of total RNA isolated from HeLa-T4+ cells transiently transfected with the subgenomic splicing reporter shown in panel A or its mutant derivate at 24 h posttransfection. Cells were cotransfected with SVctat and pXGH5 (GH1). The primer pairs used are indicated on the left (see panel A). Every band was isolated from the gel and confirmed by sequencing analysis. Transcript isoforms are depicted on the right. To compare the total RNA amount and transfection efficiency, a separate RT-PCR was performed by using primer pair 2263/2858 to amplify a spliced GH1 sequence. PCR amplicons were separated on a nondenaturing 10% polyacrylamide gel and stained with ethidium bromide. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR of total RNA from panel B using exon junction primers specific for vif mRNA (3395/3396). The authentic splice pattern (wt) was set to 100%. The relative splice site usage was normalized to cotransfected GH1.
