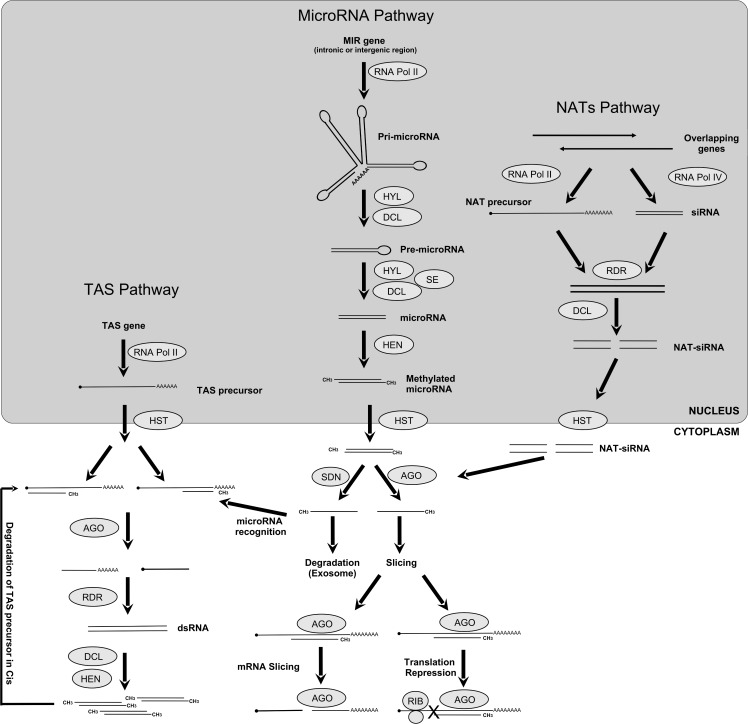
Figure 1.
General view of the small RNA pathways in plants. Cis/Trans-Acting small interfering RNAs (TAS) Pathway: A TAS gene is transcribed by RNA Pol II into a TAS precursor, later this precursor is recognized by a complementary siRNA and sliced by Argonaute (AGO) proteins into small RNA which serves as a template for RNA Dependent RNA Polymerases (RDR) to make dsRNAs. This siRNA duplex originated by Dicer-Like directs cleavage of the TAS precursor in cis, or another target mRNAs in trans. MicroRNA Pathway: A MIR gene, usually located in intergenic or intronic region, is transcribed by RNA Pol II into a precursor RNA named pri-microRNA, which is stabilized and cleaved by a protein complex composed by Dicer-like proteins (DCL) and Hyponastic Leaves (HYL) into a pre-microRNA which is further processed by the same complex plus Serrate (SE) into a mature microRNA. The HUA Enhancer (HEN) methylates the resulting mature microRNA form in the 2’-hydroxy termini of both strands. This methylated mature form is exported to cytoplasm through HASTY protein (HST). Once in the cytoplasm, AGO proteins recognize one strand of the mature microRNA and direct it to the target gene. Later, the AGO can induce the slicing of mRNA target or repress the translation complex. The other microRNA strand is directed to the Exosome and degraded by Small RNA Degrading Nuclease (SDN). Natural Acting Small RNAs (NAT) Pathway: Overlapping genes can be transcribed by RNA Pol II, resulting in a NAT precursor complementary to an siRNA, which serves as a template to the RDR proteins. The DCL protein cleaves this double-stranded precursor into dsRNAs, which are exported to the cytosol by HST protein. The NAT-siRNAs loaded into AGO complexes induce mRNA degradation in the same way as for microRNA pathway.