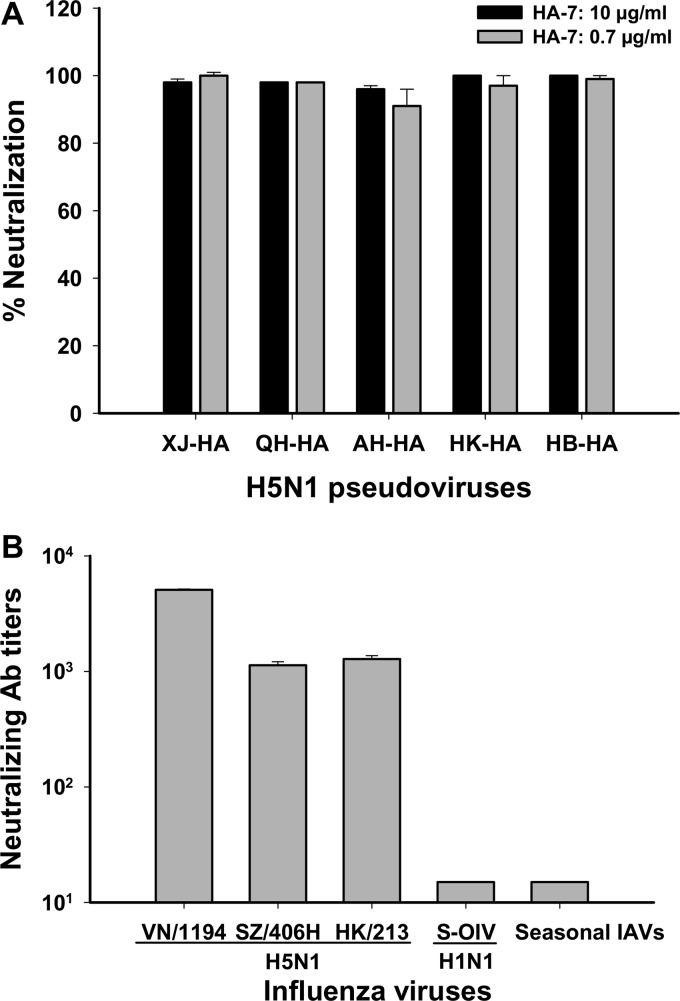
Fig 1.
Detection of inhibitory activity of MAb HA-7 on influenza virus entry by neutralization assays. (A) Pseudovirus neutralization assay. The data are presented as the mean percentages of neutralization ± standard deviations for duplicate wells of MAb HA-7 at concentrations of 0.7 and 10 μg/ml, respectively, against HAs of H5N1 pseudovirus covering four different clades, including homologous strain AH-HA (clade 2.3.4) and heterologous strains HK-HA (clade 0), XJ-HA (clade 2.2), QH-HA (clade 2.2), and HB-HA (clade 2.3.2.1). (B) Live-virus-based neutralization assay. Shown are data for neutralizing activities of HA-7 against strains VN/1194 (clade 1), SZ/406H (clade 2.3.4), and HK/213 (clade 1) of H5N1; S-OIV H1N1 (A/Beijing/501/2009 pdm strain); and seasonal IAVs. The neutralizing antibody titer was defined as the highest dilution of MAb that completely suppressed the virus-induced CPE in 50% of the wells. Panels A and B show representative data from three independent repeat experiments.