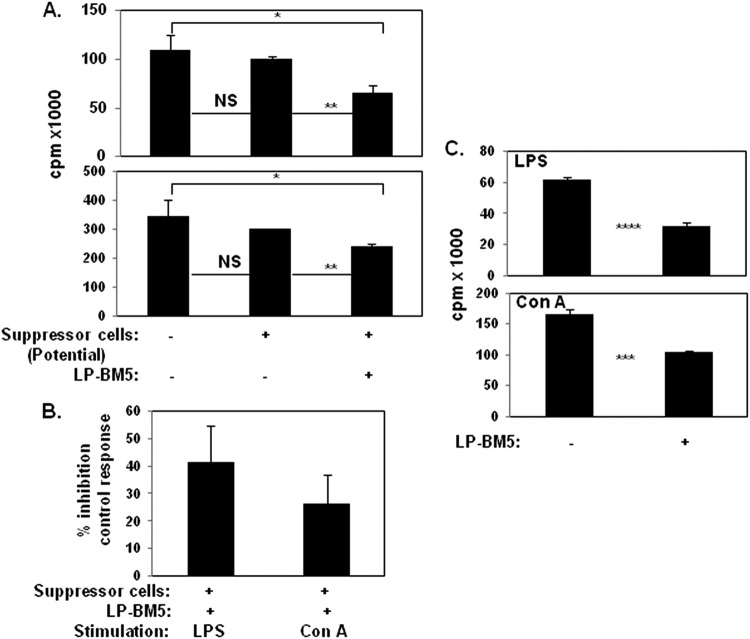
Fig 1.
Unfractionated spleen cells obtained from 5-w.p.i. LP-BM5 C57BL/6 mice inhibit in vitro B- and T-cell proliferation. (A) Naïve B6 responder (R) spleen cells only or mixed with spleen cells from uninfected (control) or 5-w.p.i. LP-BM5 mice (to test their potential as suppressor[s]) at a responder-to-suppressor (R/S) ratio of 3:1 were stimulated for 3 days with the B-cell mitogen LPS or the T-cell mitogen ConA (see Materials and Methods). After scintillation counting, [3H]thymidine incorporation is expressed as raw counts per minute (cpm). The presented pattern of results is representative of one additional experiment. (B) cpm values are converted to the percentage of inhibition of the control response as the standard form of presentation for the subsequent figures (see Materials and Methods). (C) Spleen cells from 5-w.p.i. LP-BM5 B6 mice (a pool of 3) were evaluated for MAIDS by the standard disease parameters, including immunodeficiency as measured by the ability to respond to LPS or ConA stimulation. Shown are the averages ± the SD of the percentage of inhibition of the control response for panels A and B (five experiments) and panel C (two experiments). Significance levels: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; and ****, P < 0.0001.