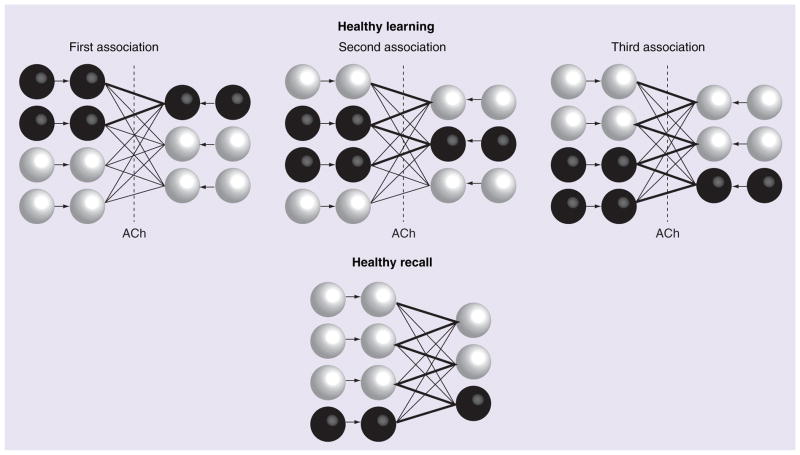
Figure 2. Illustration of network dynamics during learning and recall under normal (non-Alzheimer’s disease) conditions.
ACh helps limit activity from spreading through previously potentiated synapses as the second and third associations are learned. This prevents extra units from activating and having their connections strengthened. During recall, only the correct output unit activates. See Figure 1 for a description of the schematic representation.
ACh: Acetylcholine.
Adapted from [8] with permission from Elsevier.