Figure 3.
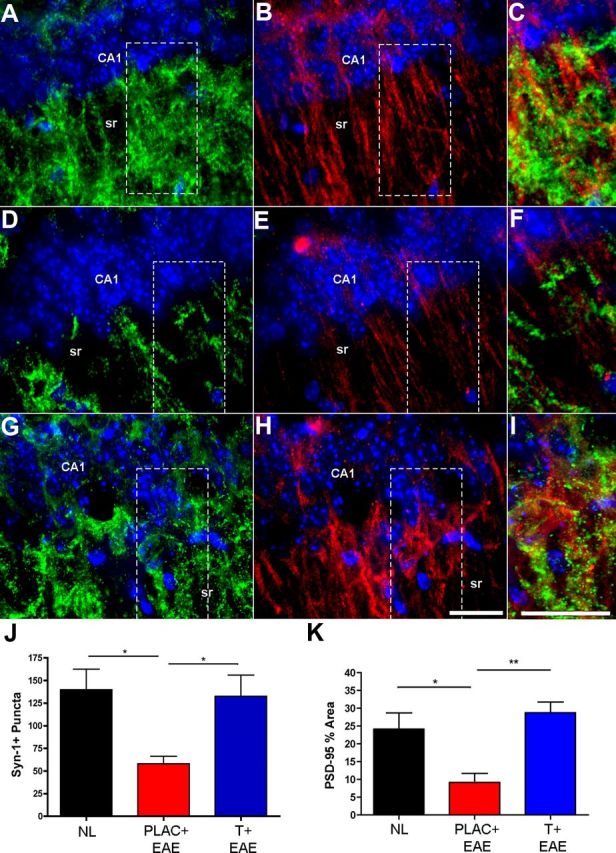
Synaptic staining in the hippocampus is disrupted in EAE and preserved with testosterone treatment. A–I, Fluorescent images depict representative hippocampal sections from healthy (A–C), placebo-treated EAE (D–F), and testosterone-treated EAE (G–I) mice, where Synapsin-1 (Syn-1; Cy3-green), PSD-95 (Cy5-red), and DAPI (blue) staining are shown at 60× magnification. During EAE, Syn-1+ puncta were significantly decreased in the CA1 region of the hippocampus (D), compared with healthy controls (A). This decrease was prevented with testosterone treatment during EAE (G), quantified in J. Similarly, PSD-95 was also significantly decreased in placebo-treated EAE mice, and preserved in testosterone-treated EAE mice (B, E, H, respectively, and quantified in K). C, F, I, Merged images of both presynaptic (Syn-1) and postsynaptic (PSD-95) staining in selected areas (dashed square) of CA1 sr demonstrate the extent of colocalization within CA1 dendrites. One-way ANOVA and Newman–Keuls post hoc analysis revealed statistical significance in presynaptic and postsynaptic integrity where *p = 0.04, n = 3 mice per group, and **p < 0.001, n = 3 mice per group. Scale bars, 10 μm.
