FIGURE 4:
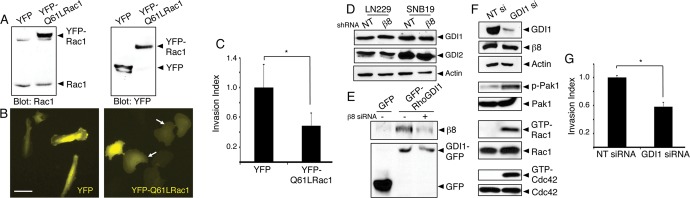
Rac1 hyperactivation or RhoGDI1 inactivation leads to impaired GBM cell invasion. (A) Lysates from LN229 cells expressing YFP or YFP-tagged Q61L-Rac1 were immunoblotted with anti-Rac1 (left) or anti-GFP (right) antibodies, revealing similar levels of expression. (B) Images of LN229 cells expressing YFP (left) or YFP-tagged Q61L-Rac1 (right). Note the flattened morphologies of cells expressing Q61L-Rac1 (arrows). Scale bar, 60 μm. (C) Quantitation of three-dimensional invasive capacities of LN229 cells expressing YFP or YFP-Q61L-Rac1; *p < 0.05. (D) SNB19 and LN229 cells expressing scrambled shRNAs or β8 shRNAs were analyzed for endogenous RhoGDI1 and RhoGDI2 protein expression. Levels of RhoGDI proteins are not altered in cells expressing β8 shRNAs. (E) LN229 cells transfected with plasmids expressing GFP or GFP-tagged RhoGDI1 were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP monoclonal antibodies and immunoblotted with anti-β8 integrin antibodies (top) or anti-GFP polyclonal antibodies (bottom). Note that β8 integrin and RhoGDI1 proteins coimmunoprecipitate, and these associations are reduced in LN229 cells expressing β8 siRNAs. (F) LN229 cells expressing scrambled siRNAs or siRNAs targeting RhoGDI1 were analyzed for RhoGDI1 protein expression. Silencing RhoGDI1 leads to elevated levels of phosphorylated Pak1 and increased levels of GTP-bound Rac1 and Cdc42. (G) Invasive behavior of LN229 cells expressing nontargeting siRNAs or RhoGD1 siRNAs quantified in invasion assays; *p < 0.05.
